CHINT – 2 Days to CIMF: A Preview of CHINT’s Melody of Manufacturing
Entering the digital era, we’re dedicated to fueling a boundless energy world.
We capture and blend the rhythmic sounds of CHINT’s factories from the whole industrial chain.
Join us for a 2-minute preview and witness the mesmerizing fusion of industry and art!
Watch the YouTube Video: NEXUS – Melody of CHINT Intelligent Manufacturing


SourceCHINT Global
EMR Analysis
More information on CHINT: See the full profile on EMR Executive Services
More information on Nan Cunhui (Chairman, CHINT Group): See the full profile on EMR Executive Services
More information on Lily Zhang (Executive President, CHINT Electrics and President, CHINT Global): See the full profile on EMR Executive Services
More information on TÜV (Technischer Überwachungsverein): https://www.tuv.com/world/en/ + TÜV are internationally active, independent service companies from Germany and Austria that test, inspect and certify technical systems, facilities and objects of all kinds in order to minimize hazards and prevent damages. The TÜV companies are organized into three large holding companies, TÜV Nord, TÜV Rheinland and TÜV SÜD (with TÜV Hessen), along with the smaller independent companies TÜV Thüringen, TÜV Saarland and TÜV Austria.
- TÜV Nord: https://www.tuev-nord-group.com/en/home/ + As a knowledge company, we have our sights firmly set on the digital future. Whether engineers, IT security experts or specialists for the mobility of the future: We ensure that our customers become even more successful in the networked world worldwide.
- More information on Dr. Dirk Stenkamp (Chairman of the Board of Management, TÜV Nord, TÜV): https://www.tuev-nord-group.com/en/company/annual-reports-facts-and-figures/annual-report-2021/the-group-executive-committee/
- TÜV Rheinland: https://www.tuv.com/world/en/ + TÜV Rheinland stands for safety and quality in virtually all areas of business and life. Founded almost 150 years ago, the company is one of the world’s leading testing service providers with more than 20,600 employees and annual revenues of around 2 billion euros. TÜV Rheinland’s highly qualified experts test technical systems and products around the world, support innovations in technology and business, train people in numerous professions and certify management systems according to international standards. In doing so, the independent experts generate trust in products as well as processes across global value-adding chains and the flow of commodities. Since 2006, TÜV Rheinland has been a member of the United Nations Global Compact to promote sustainability and combat corruption.
- More information on Dr.-Ing. Michael Fübi (Chairman of the Board of Management, TÜV Rheinland, TÜV): https://www.tuv.com/world/en/about-us/organisation-and-bodies/profiles/michael-f%C3%BCbi.html +
- TÜV SÜD: https://www.tuvsud.com/de-ch + Digital transformation is already revolutionizing every aspect of our everyday lives. It is changing the way we live, work and spend our free time. In this time of change, TÜV SÜD is committed to creating value for governments, businesses and consumers worldwide. Our goal is to inspire trust in technologies and enable progress by managing technical risks and facilitating change. This commitment is reflected in our new claim “More value. More trust.”
- More information on Dr. Johannes Bussmann (Chairman of the Board of Management, TÜV SÜD, TÜV): https://www.tuvsud.com/de-ch/ueber-uns/leadership
More information on Prabhu Ramkumar (Vice President, Head of Sustainability, TÜV SÜD North Asia, TÜV): https://www.linkedin.com/in/prabhu-ramkumar-b99b322/
More information on ASG (Albright Stonebridge Group): https://www.albrightstonebridge.com/ + ASG, part of Dentons Global Advisors, is the premier global strategic advisory and commercial diplomacy firm.
We offer perspectives honed at the highest levels of government and business, and insights informed by an unparalleled worldwide network of regional experts and sectoral specialists based in over 40 countries.
We help our clients make well informed decisions, secure opportunities, and overcome challenges with the benefit of sound judgment and a singular breadth and depth of expertise.
As a founding member of Dentons Global Advisors, ASG offers our clients access to an integrated range of advisory services spanning commercial, reputational, financial, regulatory, and governance dimensions.
More information on Kenneth Jarrett (Senior Advidsor, ASG): https://www.albrightstonebridge.com/team/kenneth-jarrett +
More information on The Economist Intelligence Unit (EIU): https://www.eiu.com/n/ + We are the research and analysis division of The Economist Group, the sister company to The Economist newspaper. Created in 1946, we have over 70 years’ experience in helping businesses, financial firms and governments to navigate the ever-changing global landscape.
More information on Mattie Bekink (China Director, Economist Intelligence Corporate Network, EIU): https://www.eiu.com/n/people/mattie-bekink/ + https://www.linkedin.com/in/mattie-bekink-6a26ab47/
EMR Additional Notes:
- Grid, Microgrids and DERs:
- The power grid is a network for delivering electricity to consumers. The power grid includes generator stations, transmission lines and towers, and individual consumer distribution lines.
- The grid constantly balances the supply and demand for the energy that powers everything from industry to household appliances.
- Electric grids perform three major functions: power generation, transmission, and distribution.
- A microgrid is a small-scale power grid that can operate independently or collaboratively with other small power grids. The practice of using microgrids is known as distributed, dispersed, decentralized, district or embedded energy production.
- Smart Grid is any electrical grid + IT at all levels . Micro Grid is a group of interconnected loads and DERs (Distributed energy resources) within a clearly defined electrical and geographical boundaries witch acts as a single controllable entity with respect to the main grid.
- Distributed energy resources (DERs) are small-scale electricity supply (typically in the range of 3 kW to 50 MW) or demand resources that are interconnected to the electric grid. They are power generation resources and are usually located close to load centers, and can be used individually or in aggregate to provide value to the grid.
- Common examples of DERs include rooftop solar PV units, natural gas turbines, microturbines, wind turbines, biomass generators, fuel cells, tri-generation units, battery storage, electric vehicles (EV) and EV chargers, and demand response applications.
- Distributed energy resources management systems (DERMS) are platforms which helps mostly distribution system operators (DSO) manage their grids that are mainly based on distributed energy resources (DER).
- DERMS are used by utilities and other energy companies to aggregate a large energy load for participation in the demand response market. DERMS can be defined in many ways, depending on the use case and underlying energy asset.
- Energy Storage System (ESS):
- An energy storage system, often abbreviated as ESS, is a device or group of devices assembled together, capable of storing energy in order to supply electrical energy at a later time. Battery ESS are the most common type of new installation and are the focus of our free fact sheet.
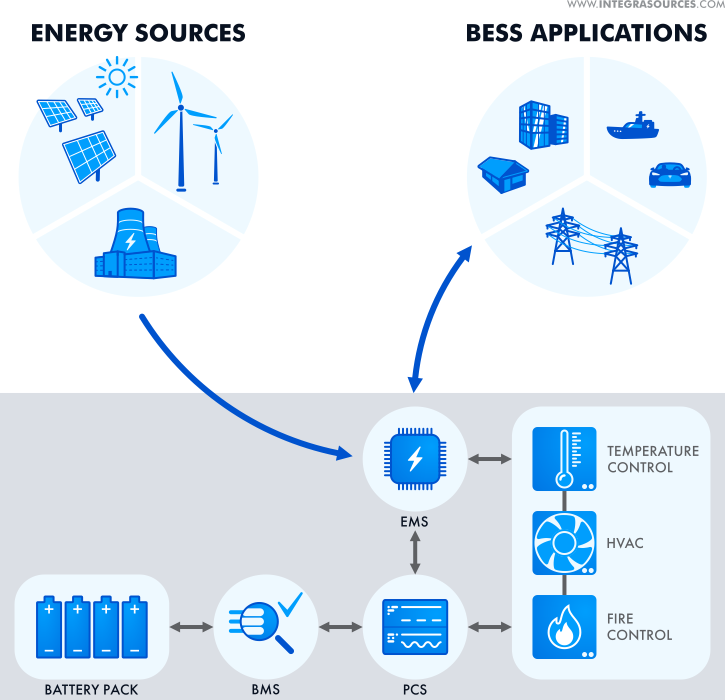
- Battery Energy Storage System (BESS):
- A BESS is an energy storage system (ESS) that captures energy from different sources, accumulates this energy, and stores it in rechargeable batteries for later use.
- Carbon Dioxide (CO2):
- Primary greenhouse gas emitted through human activities. Carbon dioxide enters the atmosphere through burning fossil fuels (coal, natural gas, and oil), solid waste, trees and other biological materials, and also as a result of certain chemical reactions (e.g., manufacture of cement). Carbon dioxide is removed from the atmosphere (or “sequestered”) when it is absorbed by plants as part of the biological carbon cycle.
- Decarbonization:
- Reduction of carbon dioxide emissions through the use of low carbon power sources, achieving a lower output of greenhouse gasses into the atmosphere.
- Low-Voltage (LV):
- The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) defines supply system low voltage as voltage in the range 50–1000 V AC or 120–1500 V DC.
- Medium-Voltage (MV):
- Medium-voltage circuit breakers rated between 1 and 35/72 kV.
- High-Voltage (HV):
- The International Electrotechnical Commission define high voltage as above 1000 V for alternating current, and at least 1500 V for direct current.
- Super High-Voltage:
- Is >300kV.
- Ultra High-Voltage:
- Is >1.000kV.


