Rittal – “IT Award 2023”: Rittal named best provider for cooling
Between April and August, over 70,000 readers voted on their favourite IT companies of the year.
Vogel IT-Medien selected winners in a total of 42 categories at the 2023 IT Awards. At a celebratory awards ceremony in Augsburg on 26 October, Rittal won the platinum award in the “Cool Cooling” category, honouring the company as the best provider of IT cooling solutions. Its seven respected specialist portals for IT professionals are DataCenter-Insider, BigData-Insider, CloudComputing-Insider, Dev-Insider, IP-Insider, Security-Insider and Storage-Insider.
When selecting its shortlist, the editorial team focused on IT firms who had stood out for their innovative talents, pioneering strategies or market sensitivity between 2022 and 2023. Readers of Vogel IT-Medien’s seven Insider portals were then able to vote for their favourites or even submit their nominations. The 2023 IT Awards were awarded in these six categories: “Cool Cooling”, “Datacenter Automation”, “Green Co-Location”, “HPC and AI Hardware”, “Intelligent Facility Components”, “Multicloud Platforms”.
Rittal was presented with the Platinum Award in the “Cool Cooling” category as the top provider of IT cooling solutions. It was followed by Stulz and Thomas-Kreen.AG, who were awarded gold and silver.
“We are delighted to have won this prestigious award, which once again confirms our skills in successfully developing IT cooling solutions and their high level of acceptance by the market,” explains Martin Dörrich, Head of the Product Management IT Group at Rittal, who accepted the award in person.
Rittal develops needs-based and innovative IT cooling solutions ranging from individual racks, to the climate control of suites and rooms, and through to customised climate control systems for sophisticated high-performance computing (HPC). With its IT cooling portfolio, the system provider meets the demand for intelligent and energy-efficient cooling.
Martin Dörrich (Center), Head of the IT Product Management Group at Rittal: “We are delighted to have won this incredible award, which once again confirms our skills in successfully developing IT cooling solutions and their high level of acceptance by the market.”
Cooler containers and water-cooling
To give just one example, Rittal provides data centre containers with energy-saving Blue e+ cooling technology. Thanks to an outdoor cooling solution on the container exterior – which is based on proven Blue e+ industrial technology – there is now more space inside the modular container for the growing amount of IT, which also results in more potential for flexible application expansion. And all of this is achieved under simple and energy-efficient installation conditions.
Efficiency is also a focus in the international Open Computer Project (OCP), which is breaking new ground with direct current technology and standardisation. As a co-developer of the standardised Open Rack V3, Rittal now also offers cooling solutions tailored to the new generations of high-performance processors (GPUs). Lots of processing power calls for efficient cooling, particularly for the increasing number of artificial intelligence applications. This generates a huge amount of heat directly in the processor, which requires effective liquid cooling. Here, Rittal offers its customers a bespoke single-phase package solution with a high level of availability and simple serviceability. Based on the power supply, the server in the OCP rack is simply connected to standardised connections to the water circuit’s central inlets and outlets.
SourceRittal
EMR Analysis
More information on The Friedhelm Loh Group: See the full profile on EMR Executive Services
More information on Prof. Friedhelm Loh (Owner and Chief Executive Officer, The Friedhelm Loh Group): See the full profile on EMR Executive Services
More information on Rittal: See the full profile on EMR Executive Services
More information on Markus Asch (Chief Executive Officer, Rittal International and Rittal Software Systems + Chairman of the Management Board, the Friedhelm Loh Group): See the full profile on EMR Executive Services
More information on Martin Dörrich (Head of the Product Management IT Group, Rittal, the Friedhelm Loh Group): See the full profile on EMR Executive Services
More information on Blue e+ Cooling Unit Series by Rittal: https://www.rittal.com/de_de/blue_e/plus_preview/public/en + Energy Efficiency through hybrid technology.
Hybrid technology: Ploneering climate control with Energy Efficiency up to 75%
- Average energy savings of 75%
- Active cooling circuit with speed-regulated components for demand-based cooling
- Integral heat pipe for passive cooling
- Constant temperature inside the enclosure
- Component-friendly cooling for a longer service life
More information on Vogel IT-Medien: https://www.vogel.de/ + From specialist publisher to Communications Group
The Vogel Communications Group (VCG), with 790 employees and around 100 million in sales, is a leading provider of specialist communication and specialist information. The group of companies is represented at 9 locations in German-speaking countries, as well as internationally with a focus on China. VCG offers a group agency network of 8 communications agencies and service companies. It is anchored with around 100 specialist media in the 5 economic fields of automotive, industry, information technology, law/business/taxes and B2B communication/marketing. The VCG offers 250+ services, 100+ digital platforms and communities as well as 300+ business events per year for professional and successful corporate communication.
More information on Matthias Bauer (Chief Executive Officer, Vogel Communications Group): https://www.vogel.de/ + https://www.linkedin.com/in/bauer-matthias/
More information on Open Compute Project (OCP): https://www.opencompute.org/ + The Open Compute Project (OCP) is a collaborative community focused on redesigning hardware technology to efficiently support the growing demands on compute infrastructure.
More information on George Tchaparian (Chief Executive Officer, Open Compute Project (OCP)): https://www.opencompute.org/about/foundation-staff + https://www.linkedin.com/in/george-tchaparian-b1640a1/
EMR Additional Notes:
- Information Technology (IT) & Operational Technology (OT):
- Information technology (IT) refers to anything related to computer technology, including hardware and software. Your email, for example, falls under the IT umbrella. This form of technology is less common in industrial settings, but often constitutes the technological backbone of most organizations and companies. These devices and programs have little autonomy and are updated frequently.
- Operational technology (OT) refers to the hardware and software used to change, monitor, or control physical devices, processes, and events within a company or organization. This form of technology is most commonly used in industrial settings, and the devices this technology refers to typically have more autonomy than information technology devices or programs. Examples of OT include SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition).
- => The main difference between OT and IT devices is that OT devices control the physical world, while IT systems manage data.
- High-Performance Computing (HPC):
- High Performance Computing (HPC) encompasses solutions that are able to process data and execute calculations at a rate that far exceeds other computers. This aggregate computing power enables different science, business, and engineering organizations to solve large problems that would otherwise be unapproachable.
- One of the best-known types of HPC solutions is the supercomputer. A supercomputer contains thousands of compute nodes that work together to complete one or more tasks. This is called parallel processing. It’s similar to having thousands of PCs networked together, combining compute power to complete tasks faster.
- High-Performance Processors and GPU:
- High-performance computing is a technique of processing massive amounts of data and performing complex calculations at high speeds. A GPU is a specialized processing unit with enhanced mathematical computation capability, making it ideal for HPC applications.
- Graphics processing units (GPUs) offer a parallel architecture and high performance that speed up certain computing processes, especially those related to artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) models. Combining GPUs with HPC clusters can increase the processing power of data centers.
- While GPUs can process data several orders of magnitude faster than a CPU due to massive parallelism, GPUs are not as versatile as CPUs. CPUs have large and broad instruction sets, managing every input and output of a computer, which a GPU cannot do.
- AI – Artificial Intelligence:
- https://searchenterpriseai.techtarget.com/definition/AI-Artificial-Intelligence +
- Artificial intelligence is the simulation of human intelligence processes by machines, especially computer systems. Specific applications of AI include expert systems, natural language processing, speech recognition and machine vision.
- As the hype around AI has accelerated, vendors have been scrambling to promote how their products and services use AI. Often what they refer to as AI is simply one component of AI, such as machine learning. AI requires a foundation of specialized hardware and software for writing and training machine learning algorithms. No one programming language is synonymous with AI, but a few, including Python, R and Java, are popular.
- In general, AI systems work by ingesting large amounts of labeled training data, analyzing the data for correlations and patterns, and using these patterns to make predictions about future states. In this way, a chatbot that is fed examples of text chats can learn to produce lifelike exchanges with people, or an image recognition tool can learn to identify and describe objects in images by reviewing millions of examples.
- AI programming focuses on three cognitive skills: learning, reasoning and self-correction.
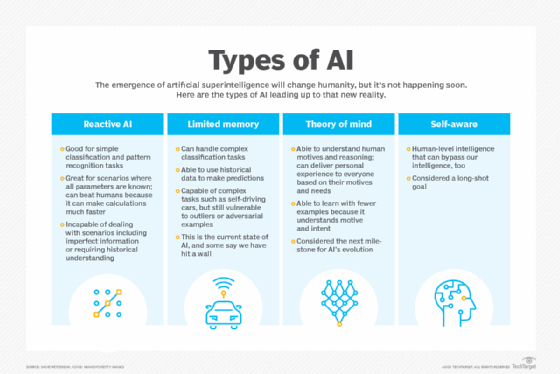
- What are the 4 types of artificial intelligence?
- Type 1: Reactive machines. These AI systems have no memory and are task specific. An example is Deep Blue, the IBM chess program that beat Garry Kasparov in the 1990s. Deep Blue can identify pieces on the chessboard and make predictions, but because it has no memory, it cannot use past experiences to inform future ones.
- Type 2: Limited memory. These AI systems have memory, so they can use past experiences to inform future decisions. Some of the decision-making functions in self-driving cars are designed this way.
- Type 3: Theory of mind. Theory of mind is a psychology term. When applied to AI, it means that the system would have the social intelligence to understand emotions. This type of AI will be able to infer human intentions and predict behavior, a necessary skill for AI systems to become integral members of human teams.
- Type 4: Self-awareness. In this category, AI systems have a sense of self, which gives them consciousness. Machines with self-awareness understand their own current state. This type of AI does not yet exist.
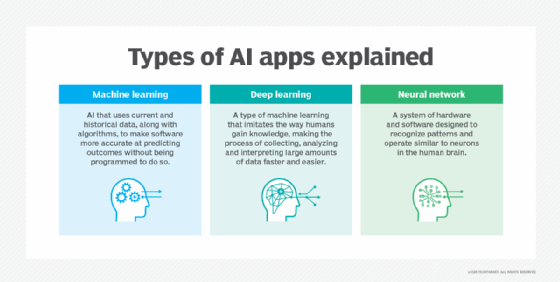
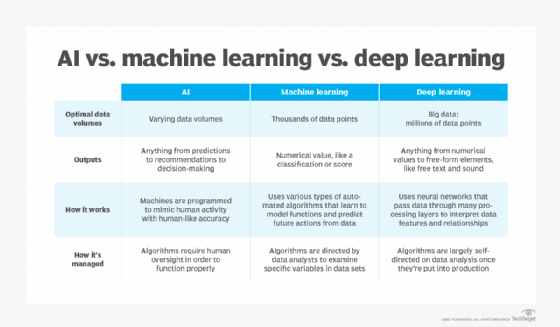
- Machine Learning:
- Developed to mimic human intelligence. It lets the machines learn independently by ingesting vast amounts of data and detecting patterns. Many ML algorithms use statistics formulas and big data to function.
- Type of artificial intelligence (AI) that allows software applications to become more accurate at predicting outcomes without being explicitly programmed to do so. Machine learning algorithms use historical data as input to predict new output values.
- Recommendation engines are a common use case for machine learning. Other popular uses include fraud detection, spam filtering, malware threat detection, business process automation (BPA) and Predictive maintenance.
- Classical machine learning is often categorized by how an algorithm learns to become more accurate in its predictions. There are four basic approaches: supervised learning, unsupervised learning, semi-supervised learning and reinforcement learning. The type of algorithm data scientists choose to use depends on what type of data they want to predict.
- Deep Learning:
- Subset of machine learning. Deep learning enabled much smarter results than were originally possible with machine learning. Consider the face recognition example.
- Deep learning makes use of layers of information processing, each gradually learning more and more complex representations of data. The early layers may learn about colors, the next ones learn about shapes, the following about combinations of those shapes, and finally actual objects. Deep learning demonstrated a breakthrough in object recognition.
- Deep learning is currently the most sophisticated AI architecture we have developed.
- Computer Vision:
- Computer vision is a field of artificial intelligence (AI) that enables computers and systems to derive meaningful information from digital images, videos and other visual inputs — and take actions or make recommendations based on that information.
- The most well-known case of this today is Google’s Translate, which can take an image of anything — from menus to signboards — and convert it into text that the program then translates into the user’s native language.
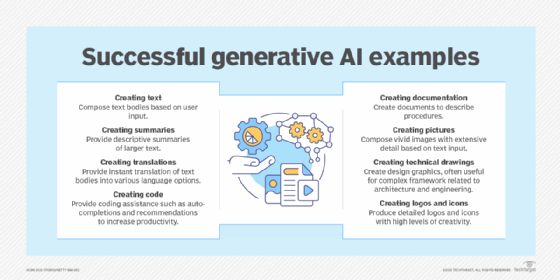
- Generative AI:
- Generative AI technology generates outputs based on some kind of input – often a prompt supplied by a person. Some GenAI tools work in one medium, such as turning text inputs into text outputs, for example. With the public release of ChatGPT in late November 2022, the world at large was introduced to an AI app capable of creating text that sounded more authentic and less artificial than any previous generation of computer-crafted text.
- https://searchenterpriseai.techtarget.com/definition/AI-Artificial-Intelligence +
- Cloud Computing:
- Cloud computing is a general term for anything that involves delivering hosted services over the internet. … Cloud computing is a technology that uses the internet for storing and managing data on remote servers and then access data via the internet.
- Cloud computing is the on-demand availability of computer system resources, especially data storage and computing power, without direct active management by the user. Large clouds often have functions distributed over multiple locations, each location being a data center.
- Edge Computing:
- Edge computing is a form of computing that is done on site or near a particular data source, minimizing the need for data to be processed in a remote data center.
- Edge computing can enable more effective city traffic management. Examples of this include optimising bus frequency given fluctuations in demand, managing the opening and closing of extra lanes, and, in future, managing autonomous car flows.
- An edge device is any piece of hardware that controls data flow at the boundary between two networks. Edge devices fulfill a variety of roles, depending on what type of device they are, but they essentially serve as network entry — or exit — points.
- There are five main types of edge computing devices: IoT sensors, smart cameras, uCPE equipment, servers and processors. IoT sensors, smart cameras and uCPE equipment will reside on the customer premises, whereas servers and processors will reside in an edge computing data centre.
- In service-based industries such as the finance and e-commerce sector, edge computing devices also have roles to play. In this case, a smart phone, laptop, or tablet becomes the edge computing device.
- Edge Devices:
- Edge devices encompass a broad range of device types, including sensors, actuators and other endpoints, as well as IoT gateways. Within a local area network (LAN), switches in the access layer — that is, those connecting end-user devices to the aggregation layer — are sometimes called edge switches.
- Data Centers:
- A data center is a facility that centralizes an organization’s shared IT operations and equipment for the purposes of storing, processing, and disseminating data and applications. Because they house an organization’s most critical and proprietary assets, data centers are vital to the continuity of daily operations.
- Hyperscale Data Centers:
- The clue is in the name: hyperscale data centers are massive facilities built by companies with vast data processing and storage needs. These firms may derive their income directly from the applications or websites the equipment supports, or sell technology management services to third parties.


