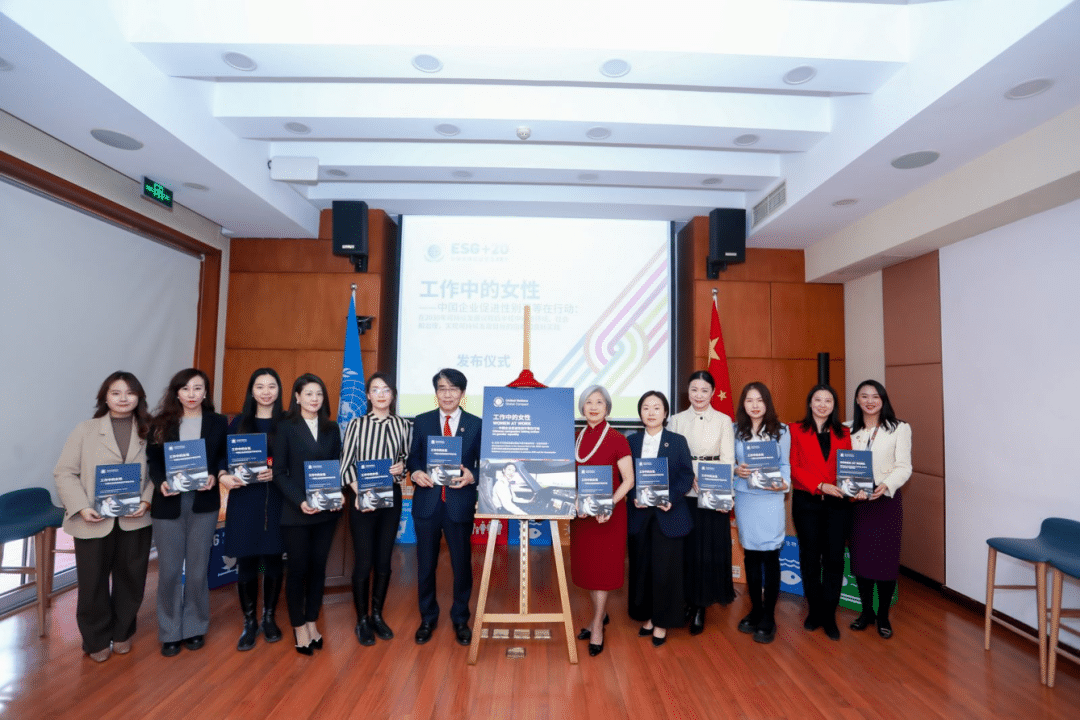
CHINT – CHINT Global & UNGC: Empower Women in Workplace
On March 8, 2024, Ms. BeiBei Zheng, Vice President of CHINT Global, was invited to attend the launch ceremony of “WOMEN AT WORK: Chinese companies taking action on gender equality — Guidance and Good Practices to Advance ESG and the Sustainable Development Goals in the Second Half of the 2030 Agenda” held in Beijing.
This event, initiated by the United Nations Global Compact, aimed to explore and share the achievements and experiences of Chinese enterprises in gender equality, creating inclusive workplaces, and implementing Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) concepts and principles.
The event also welcomed Changhee Lee, Director of the International Labour Organization for China and Mongolia, Cheng Jin, Corporate Social Responsibility expert at UNICEF, Han Ruiyun, editorial board member of the 21st Century EconomicReport, and senior representatives from case study companies such as Esquel Group, JD.com, Lenovo, and Xiamen Airlines. They participated in discussions on how enterprises can continue to contribute to the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) for 2030, offering valuable insights.
As the first report by the United Nations Global Compact focusing on the good practices of Chinese enterprises in promoting gender equality, the guide compiles cases and stories of female employees from eight Chinese enterprises, including CHINT Global. It highlights fair workplace opportunities, safe and healthy work environments, and family-friendly workplaces, showcasing specific actions and good practices undertaken by Chinese enterprises in gender equality. This provides valuable practice references for both Chinese and global enterprises, offering a practical roadmap for companies to support gender equality. Four outstanding female employees of CHINT, from different countries and in different positions, and their stories have been collected in the guide.

During the ceremony, Sanda Ojiambo, Assistant Secretary-General and CEO of the United Nations Global Compact, remarked,
“The guide released today is a roadmap for promoting gender equality in the workplace both in China and globally. As China is set to host the Global Women’s Summit in 2025, this guide will serve as a timely and practical resource.”
She emphasized the crucial role of workplace gender equality in building stronger businesses and a more just, resilient society.

Siddharth Chatterjee, the UN Resident Coordinator in China, who witnessed the launch of the guide, noted that women and girls make up half the world’s population and therefore half its potential. He said, “Based on the Women’s Empowerment Principles (WEPs) tool, this guide provides a roadmap showcasing exemplary practices that can be replicated, scaled, and guide businesses in assessing their impact on gender equality.”

Ms. BeiBei Zheng, Vice President of CHINT Global, stated at the forum that as a leading provider of smart energy system solutions, CHINT has always integrated ESG principles into its corporate governance to achieve sustainable development. The recent “CHINT’s Gender Equality Statement” in response to the guide’s launch demonstrates CHINT’s commitment to promoting gender equality and sustainable development.
Ms. Beibei Zheng also highlighted that as society progresses and awareness of gender equality increases, more women are making significant contributions in the fields of technology and new energy. CHINT fosters an open and inclusive corporate culture, not only nurturing female talent in areas like photovoltaic technology and overseas sales but also encouraging partners and supply chain members to commit to gender equality, thus promoting sustainable development across the industry.
Looking ahead, CHINT will continue to focus on gender equality and diversity, providing equal opportunities and support for women and working with partners to advance the gender equality process.
SourceCHINT Global
EMR Analysis
More information on CHINT: See the full profile on EMR Executive Services
More information on Nan Cunhui (Chairman, Zhengtai Group + Chairman, CHINT Group): See the full profile on EMR Executive Services
More information on Lily Zhang (Executive President, CHINT Electric + President and Chief Executive Officer, CHINT Global): See the full profile on EMR Executive Services
More information on Beibei Zheng (Vice President, CHINT Global): See the full profile on EMR Executive Services
More information on the United Nations: https://www.un.org/ + Peace, dignity and equality on a healthy planet.
The United Nations is an international organization founded in 1945. Currently made up of 193 Member States, the UN and its work are guided by the purposes and principles contained in its founding Charter.
The UN has evolved over the years to keep pace with a rapidly changing world.
But one thing has stayed the same: it remains the one place on Earth where all the world’s nations can gather together, discuss common problems, and find shared solutions that benefit all of humanity.
The main parts of the UN structure are the General Assembly, the
Security Council, the Economic and Social Council, the Trusteeship Council, the International Court of Justice, and the UN Secretariat. All were established in 1945 when the UN was founded.
More information on António Guterres (Secretary-General, United Nations): https://www.un.org/sg/en/content/sg/biography
More information on the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDG):
- United Nations Global Compact (UNGC): https://www.unglobalcompact.org + The world’s largest corporate sustainability initiative: a call to companies to align strategies in operations with universal principles on human rights, labour, environment and anti corruption, and take actions that advance societal goals.
- At the UN Global Compact, we aim to mobilize a global movement of sustainable companies and stakeholders to create the world we want. That’s our vision.
- To make this happen, the UN Global Compact supports companies to:
- Do business responsibly by aligning their strategies and operations with Ten Principles on human rights, labour, environment and anti-corruption; and
- Take strategic actions to advance broader societal goals, such as the UN Sustainable Development Goals, with an emphasis on collaboration and innovation.
- To make this happen, the UN Global Compact supports companies to:
- United Nations Global Compact 10 Principles:
- Human Rights
- Principle 1: Businesses should support and respect the protection of internationally proclaimed human rights; and
- Principle 2: make sure that they are not complicit in human rights abuses.
- Labour
- Principle 3: Businesses should uphold the freedom of association and the effective recognition of the right to collective bargaining;
- Principle 4: the elimination of all forms of forced and compulsory labour;
- Principle 5: the effective abolition of child labour; and
- Principle 6: the elimination of discrimination in respect of employment and occupation.
- Environment
- Principle 7: Businesses should support a precautionary approach to environmental challenges;
- Principle 8: undertake initiatives to promote greater environmental responsibility; and
- Principle 9: encourage the development and diffusion of environmentally friendly technologies.
- Anti-Corruption
- Principle 10: Businesses should work against corruption in all its forms, including extortion and bribery.
- Human Rights
- The 17 SDGS (Sustainable Development Goals) by 2030:
- Detailed explanation of each of the 17 SDGS: https://www.unglobalcompact.org/sdgs/17-global-goals

More information on Sanda Ojiambo (Assistant Secretary-General and Chief Executive Officer, UN Global Compact, United Nations): https://www.un.org/sg/en/content/profiles/sanda-ojiambo + https://unglobalcompact.org/about/governance/asg-ceo + https://www.linkedin.com/in/sandaojiambo/
More information on Siddharth Chatterjee (Resident Coordinator in China, United Nations): https://china.un.org/en/about/about-the-resident-coordinator-office + https://www.linkedin.com/in/siddharthchatterjee1un/
EMR Additional Notes:
- ESG (Environmental, Social and Governance):
- Refers to the three key factors when measuring the sustainability and ethical impact of an investment in a business or company. Most socially responsible investors check companies out using ESG criteria to screen investments.
- ESG metrics are not commonly part of mandatory financial reporting, though companies are increasingly making disclosures in their annual report or in a standalone sustainability report.
- There is not a standardized approach to the calculation or presentation of different ESG metrics.
- Environmental: Conservation of the natural world
- Climate change and carbon emissions
- Air and water pollution
- Biodiversity
- Deforestation
- Energy efficiency
- Waste management
- Water scarcity
- …
- Social: Consideration of people & relationships
- Customer satisfaction
- Data protection and privacy
- Gender and diversity
- Employee engagement
- Community relations
- Human rights
- Labor standards
- …
- Governance: Standards for running a company
- Board composition
- Audit committee structure
- Bribery and corruption
- Executive compensation
- Lobbying
- Political contributions
- Whistleblower schemes
- …
- Environmental: Conservation of the natural world
- Criteria are of increasing interest to companies, their investors and other stakeholders. With growing concern about he ethical status of quoted companies, these standards are the central factors that measure the ethical impact and sustainability of investment in a company.
- Consequently, ESG analysis considers how companies serve society and how this impacts their current and future performance.
- CSR (Corporate Social Responsibility):
- Framework or business model that helps a company be socially accountable to itself, its stakeholders, and the public.
- The purpose of CSR is to give back to the community, take part in philanthropic causes, and provide positive social value. Businesses are increasingly turning to CSR to make a difference and build a positive brand around their company.
- CSR tends to target opinion formers – politicians, pressure groups, media. Sustainability targets here the whole value chain – from suppliers to operations to partners to end-consumers.
- CSR vs. ESG:
- CSR is a company’s framework of sustainability plans and responsible cultural influence, whereas ESG is the assessable outcome concerning a company’s overall sustainability performance.
- The major difference between them is that CSR is a business model used by individual companies, while ESG is a criteria that investors use to assess a company and determine if they are worth investing in.


