CHINT – CHINT’s Sustainability Strategy Workshop Held Successfully
Making green last forever, every step of our quest today is a thoughtful consideration for the long-term future.
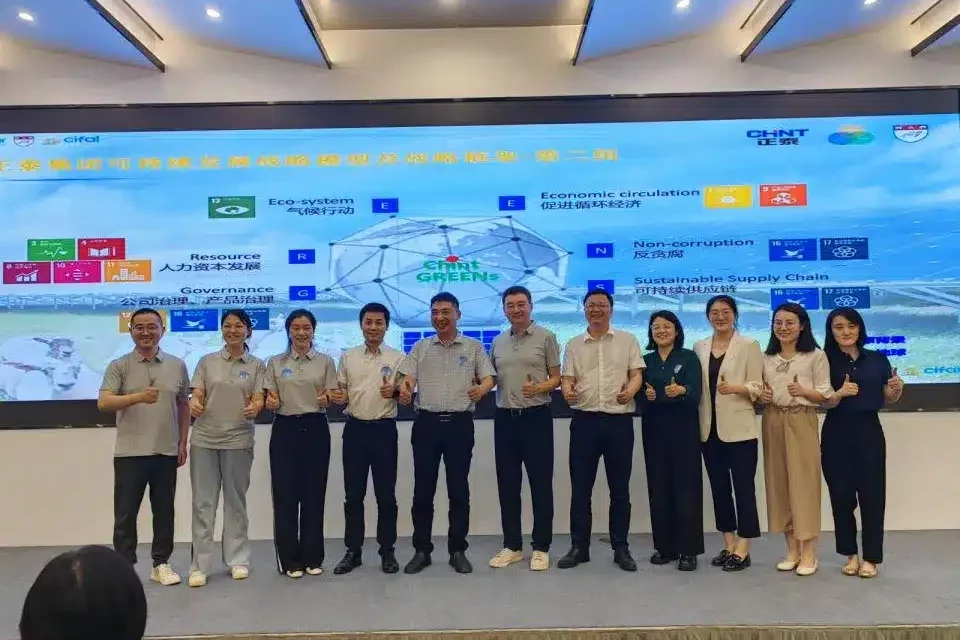
On 13th-14th September, CHINT’s Sustainable Development Workshop was successfully held. The workshop focused on the global ESG development trend, the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), corporate ESG development management and other thematic contents. Core members of CHINT’s various departments gathered together to carry out two-day training and exchange, and ultimately constructed the CHINT’s sustainable development strategy framework for the year 2030.
The workshop invited relevant experts from the United Nations Institute for Training and Research (UNITAR) to report and share. Participants in the workshop included core members of the Sustainability Office of CHINT, heads of CHINT Procurement Department, Securities Department, Overseas Market Department, Compliance Department, Strategic Investment Department, President’s Office, and other departments, as well as CHINT various industrial companies.
At the workshop, Li Ming, General Manager of Marketing Department of CHINT Group, firstly made a comprehensive compendium of the connotation of ESG and the global development situation, and put forward the risks and opportunities of sustainable development faced by enterprises. Li Ming stressed that promoting ESG strategy is not only a systematic project involving all levels of the Group, but also a dynamic process that requires long-term persistence and continuous optimisation. It involves all aspects of the Group, including but not limited to energy use, labour rights and interests, product responsibility and corporate governance. The complexity and difficulty of these topics are self-evident, and they also require companies to constantly innovate their thinking, update their technology and improve their management in order to adapt to the fast-changing external environment and increasingly stringent regulatory requirements. Then Wang Hong, an expert from the United Nations Institute for Training and Research (UNITAR), took the ESG practice of Yum China Ltd. as a case study, and shared the specific methods of integrating ESG into the development strategy of an enterprise, including how to enhance the performance and international influence of an enterprise’s sustainable development through the establishment of an enterprise’s ESG management system, the selection of ESG KPIs, as well as the establishment of a performance management system.


During the two-day workshop, members from various departments discussed and exchanged views on ESG information disclosure, corporate ESG development needs, and ESG strategy implementation paths in different contexts, etc. Through case studies, group discussions and expert Q&A, members analysed in-depth the effectiveness of the current ESG implementation strategies, and explored how to integrate the concept of sustainable development into the overall strategy of the enterprise. In the end, the substantive issues of CHINT sustainable development were identified, the framework and implementation path of the enterprise’s sustainable development were jointly constructed, and the working direction and goals were clearly defined, contributing wisdom and strength from different departments to CHINT ESG development.


Practicing Outweighs Preaching
CHINT will endeavour to promote the wider application and practice of ESG concepts in more professional fields, give richer connotations to the SDGs with more positive actions, lead technological innovation with the concept of green development, and create a ‘zero-carbon’ future hand in hand with global partners.
CHINT Knowledge Corner
Sustainable Development originated from the Brundtland Report in 1987 and is defined as ‘the ability to meet the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs’. The core of sustainable development lies in three pillars: economic development, social inclusion, and environmental protection, and ESG is an important indicator system for measuring corporate sustainability, which is the global language for assessing corporate sustainability.

ESG stands for ‘Environmental, Social and Governance’. First coined by the United Nations Global Compact in 2004, the concept first gained traction as a reference point for investment decisions, and is often considered to be the precursor to socially responsible investing (SRI), which emerged in the 1960s and 1970s. At that time, investors and companies were driven by business ethics and began to emphasize labour rights, race and gender equality; in the 1970s and 1980s, countries such as the United States and Canada launched a vigorous environmental protection movement and passed tough environmental legislation, which gave birth to the concept of ‘sustainability’. The concept of ‘sustainability’ was born. The real milestone came in 2004, when the Global Compact released its report Who Cares Wins, officially launching the ESG concept.
SourceCHINT Global
EMR Analysis
More information on CHINT: See the full profile on EMR Executive Services
More information on Nan Cunhui (Chairman, Zhengtai Group + Chairman, CHINT Group): See the full profile on EMR Executive Services
More information on Lily Zhang (Executive President, CHINT Electric + President and Chief Executive Officer, CHINT Global): See the full profile on EMR Executive Services
More information on Li Ming (General Manager, Market Strategy Department, CHINT Electric Appliances, CHINT): See the full profile on EMR Executive Services
More information on the United Nations: https://www.un.org/ + Peace, dignity and equality on a healthy planet.
The United Nations is an international organization founded in 1945. Currently made up of 193 Member States, the UN and its work are guided by the purposes and principles contained in its founding Charter.
The UN has evolved over the years to keep pace with a rapidly changing world.
But one thing has stayed the same: it remains the one place on Earth where all the world’s nations can gather together, discuss common problems, and find shared solutions that benefit all of humanity.
The main parts of the UN structure are the General Assembly, the
Security Council, the Economic and Social Council, the Trusteeship Council, the International Court of Justice, and the UN Secretariat. All were established in 1945 when the UN was founded.
More information on António Guterres (Secretary-General, United Nations): https://www.un.org/sg/en/content/sg/biography
More information on the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDG):
- United Nations Global Compact (UNGC): https://www.unglobalcompact.org + The world’s largest corporate sustainability initiative: a call to companies to align strategies in operations with universal principles on human rights, labour, environment and anti corruption, and take actions that advance societal goals.
- At the UN Global Compact, we aim to mobilize a global movement of sustainable companies and stakeholders to create the world we want. That’s our vision.
- To make this happen, the UN Global Compact supports companies to:
- Do business responsibly by aligning their strategies and operations with Ten Principles on human rights, labour, environment and anti-corruption; and
- Take strategic actions to advance broader societal goals, such as the UN Sustainable Development Goals, with an emphasis on collaboration and innovation.
- To make this happen, the UN Global Compact supports companies to:
- United Nations Global Compact 10 Principles:
- Human Rights
- Principle 1: Businesses should support and respect the protection of internationally proclaimed human rights; and
- Principle 2: make sure that they are not complicit in human rights abuses.
- Labour
- Principle 3: Businesses should uphold the freedom of association and the effective recognition of the right to collective bargaining;
- Principle 4: the elimination of all forms of forced and compulsory labour;
- Principle 5: the effective abolition of child labour; and
- Principle 6: the elimination of discrimination in respect of employment and occupation.
- Environment
- Principle 7: Businesses should support a precautionary approach to environmental challenges;
- Principle 8: undertake initiatives to promote greater environmental responsibility; and
- Principle 9: encourage the development and diffusion of environmentally friendly technologies.
- Anti-Corruption
- Principle 10: Businesses should work against corruption in all its forms, including extortion and bribery.
- Human Rights
- The 17 SDGS (Sustainable Development Goals) by 2030:
- Detailed explanation of each of the 17 SDGS: https://www.unglobalcompact.org/sdgs/17-global-goals

More information on Sanda Ojiambo (UN Assistant Secretary-General and CEO of the UN Global Compact, United Nations): https://www.un.org/sg/en/content/profiles/sanda-ojiambo + https://unglobalcompact.org/about/governance/asg-ceo + https://www.linkedin.com/in/sandaojiambo/
More information on UNITAR (United Nations institute for Training and Research): https://www.unitar.org/ + The United Nations Institute for Training and Research (UNITAR) provides innovative learning solutions to individuals, organizations and institutions to enhance global decision-making and support country-level action for shaping a better future.
UNITAR was created in 1963 to train and equip young diplomats from newly-independent UN Member States with the knowledge and skills needed to navigate through the diplomatic environment.
Over the years, UNITAR has acquired unique expertise and experience in designing and delivering a variety of training activities. We have become a leading institute in the provision of customized and creative learning solutions to institutions and individuals from both public and private sectors.
With a strategy fully focused on achieving the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), UNITAR supports Governments to implement the 2030 Agenda.
More information on Nikhil Seth (Executive Director, UNITAR): https://www.unitar.org/about/unitar/executive-director + https://www.linkedin.com/in/nikhil-seth-78a695138/
More information on Wang Hong (Expert, UNITAR): N.A.
More information on Net Zero by 2050 by the United Nations: https://www.un.org/en/climatechange/net-zero-coalition + Put simply, net zero means cutting greenhouse gas emissions to as close to zero as possible, with any remaining emissions re-absorbed from the atmosphere, by oceans and forests for instance.
Currently, the Earth is already about 1.1°C warmer than it was in the late 1800s, and emissions continue to rise. To keep global warming to no more than 1.5°C – as called for in the Paris Agreement – emissions need to be reduced by 45% by 2030 and reach net zero by 2050.
More than 140 countries, including the biggest polluters – China, the United States, India and the European Union – have set a net-zero target, covering about 88% of global emissions. More than 9,000 companies, over 1000 cities, more than 1000 educational institutions, and over 600 financial institutions have joined the Race to Zero, pledging to take rigorous, immediate action to halve global emissions by 2030.
More information on Net Zero by 2050 by the Science Based Targets initiative (SBTi): https://sciencebasedtargets.org/net-zero + The SBTi’s Corporate Net-Zero Standard is the world’s only framework for corporate net-zero target setting in line with climate science. It includes the guidance, criteria, and recommendations companies need to set science-based net-zero targets consistent with limiting global temperature rise to 1.5°C.
UN vs. SBTi:
- UN targets nations, while SBTi focuses on companies. UN sets a broad goal, while SBTI provides a detailed framework for target setting.
- Both aim to achieve net zero emissions and limit warming to 1.5°C. The UN sets the overall direction, and SBTi helps businesses translate that goal into actionable plans.
Key components of the Corporate Net-Zero Standard:
- Near-term targets: Rapid, deep cuts to direct and indirect value-chain emissions must be the overarching priority for companies. Companies must set near-term science-based targets to roughly halve emission before 2030. This is the most effective, scientifically-sound way of limiting global temperature rise to 1.5°C.
- Long-term targets: Companies must set long-term science-based targets. Companies must cut all possible – usually more than 90% – of emissions before 2050.
- Neutralize residual emissions: After a company has achieved its long-term target and cut emissions by more than 90%, it must use permanent carbon removal and storage to counterbalance the final 10% or more of residual emissions that cannot be eliminated. A company is only considered to have reached net-zero when it has achieved its long-term science-based target and neutralized any residual emissions.
- Beyond Value Chain Mitigation (BVCM): Businesses should invest now in actions to reduce and remove emissions outside of their value chains in addition to near- and long-term science-based targets.
EMR Additional Notes:
- ESG (Environmental, Social and Governance):
- Refers to the three key factors when measuring the sustainability and ethical impact of an investment in a business or company. Most socially responsible investors check companies out using ESG criteria to screen investments.
- ESG metrics are not commonly part of mandatory financial reporting, though companies are increasingly making disclosures in their annual report or in a standalone sustainability report.
- There is not a standardized approach to the calculation or presentation of different ESG metrics.
- Environmental: Conservation of the natural world
- Climate change and carbon emissions
- Air and water pollution
- Biodiversity
- Deforestation
- Energy efficiency
- Waste management
- Water scarcity
- …
- Social: Consideration of people & relationships
- Customer satisfaction
- Data protection and privacy
- Gender and diversity
- Employee engagement
- Community relations
- Human rights
- Labor standards
- …
- Governance: Standards for running a company
- Board composition
- Audit committee structure
- Bribery and corruption
- Executive compensation
- Lobbying
- Political contributions
- Whistleblower schemes
- …
- Environmental: Conservation of the natural world
- Criteria are of increasing interest to companies, their investors and other stakeholders. With growing concern about he ethical status of quoted companies, these standards are the central factors that measure the ethical impact and sustainability of investment in a company.
- Consequently, ESG analysis considers how companies serve society and how this impacts their current and future performance.
- CSR (Corporate Social Responsibility):
- Framework or business model that helps a company be socially accountable to itself, its stakeholders, and the public.
- The purpose of CSR is to give back to the community, take part in philanthropic causes, and provide positive social value. Businesses are increasingly turning to CSR to make a difference and build a positive brand around their company.
- CSR tends to target opinion formers – politicians, pressure groups, media. Sustainability targets here the whole value chain – from suppliers to operations to partners to end-consumers.
- CSR vs. ESG:
- CSR is a company’s framework of sustainability plans and responsible cultural influence, whereas ESG is the assessable outcome concerning a company’s overall sustainability performance.
- The major difference between them is that CSR is a business model used by individual companies, while ESG is a criteria that investors use to assess a company and determine if they are worth investing in.
- Carbon Dioxide (CO2):
- Primary greenhouse gas emitted through human activities. Carbon dioxide enters the atmosphere through burning fossil fuels (coal, natural gas, and oil), solid waste, trees and other biological materials, and also as a result of certain chemical reactions (e.g., manufacture of cement). Carbon dioxide is removed from the atmosphere (or “sequestered”) when it is absorbed by plants as part of the biological carbon cycle.
- Biogenic Carbon Dioxide (CO2):
- Biogenic Carbon Dioxide (CO2) and Carbon Dioxide (CO2) are the same. Scientists differentiate between biogenic carbon (that which is absorbed, stored and emitted by organic matter like soil, trees, plants and grasses) and non-biogenic carbon (that found in all other sources, most notably in fossil fuels like oil, coal and gas).
- Decarbonization:
- Reduction of carbon dioxide emissions through the use of low carbon power sources, achieving a lower output of greenhouse gasses into the atmosphere.
- Carbon Footprint:
- There is no universally agreed definition of what a carbon footprint is.
- A carbon footprint is generally understood to be the total amount of greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions that are directly or indirectly caused by an individual, organization, product, or service. These emissions are typically measured in tonnes of carbon dioxide equivalent (CO2e).
- In 2009, the Greenhouse Gas Protocol (GHG Protocol) published a standard for calculating and reporting corporate carbon footprints. This standard is widely accepted by businesses and other organizations around the world. The GHG Protocol defines a carbon footprint as “the total set of greenhouse gas emissions caused by an organization, directly and indirectly, through its own operations and the value chain.”
- CO2e (Carbon Dioxide Equivalent):
- CO2e means “carbon dioxide equivalent”. In layman’s terms, CO2e is a measurement of the total greenhouse gases emitted, expressed in terms of the equivalent measurement of carbon dioxide. On the other hand, CO2 only measures carbon emissions and does not account for any other greenhouse gases.
- A carbon dioxide equivalent or CO2 equivalent, abbreviated as CO2-eq is a metric measure used to compare the emissions from various greenhouse gases on the basis of their global-warming potential (GWP), by converting amounts of other gases to the equivalent amount of carbon dioxide with the same global warming potential.
- Carbon dioxide equivalents are commonly expressed as million metric tonnes of carbon dioxide equivalents, abbreviated as MMTCDE.
- The carbon dioxide equivalent for a gas is derived by multiplying the tonnes of the gas by the associated GWP: MMTCDE = (million metric tonnes of a gas) * (GWP of the gas).
- For example, the GWP for methane is 25 and for nitrous oxide 298. This means that emissions of 1 million metric tonnes of methane and nitrous oxide respectively is equivalent to emissions of 25 and 298 million metric tonnes of carbon dioxide.
- Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS) – Carbon Capture, Utilisation and Storage (CCUS):
- CCS involves the capture of carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions from industrial processes. This carbon is then transported from where it was produced, via ship or in a pipeline, and stored deep underground in geological formations.
- CCS projects typically target 90 percent efficiency, meaning that 90 percent of the carbon dioxide from the power plant will be captured and stored.
- Carbon Dioxide Removal (CDR):
- Carbon Dioxide Removal encompasses approaches and methods for removing CO2 from the atmosphere and then storing it permanently in underground geological formations, in biomass, oceanic reservoirs or long-lived products in order to achieve negative emissions.
- Direct Air Capture (DAC):
- Technologies extracting CO2 directly from the atmosphere at any location, unlike carbon capture which is generally carried out at the point of emissions, such as a steel plant.
- Constraints like costs and energy requirements as well as the potential for pollution make DAC a less desirable option for CO2 reduction. Its larger land footprint when compared to other mitigation strategies like carbon capture and storage systems (CCS) also put it at a disadvantage.
- Carbon Credits or Carbon Offsets:
- Permits that allow the owner to emit a certain amount of carbon dioxide or other greenhouse gases. One credit permits the emission of one ton of carbon dioxide or the equivalent in other greenhouse gases.
- The carbon credit is half of a so-called cap-and-trade program. Companies that pollute are awarded credits that allow them to continue to pollute up to a certain limit, which is reduced periodically. Meanwhile, the company may sell any unneeded credits to another company that needs them. Private companies are thus doubly incentivized to reduce greenhouse emissions. First, they must spend money on extra credits if their emissions exceed the cap. Second, they can make money by reducing their emissions and selling their excess allowances.


