Hikvision – Hikvision launches flagship Interactive Flat Panel in online event
October 30, 2023 – The Netherlands Hikvision will unveil its new flagship Interactive Flat Panel in an online briefing session for installers, distributors, and end users.
With its highest-level processor and intelligent conference camera, this new product series pushes the boundaries of unified collaboration, primarily in the smart education and conference meeting markets.
The event will take place on Thursday 23 November 2023 at 10:00 CET, and visitors can register here.

Product experts will introduce the innovation and benefits of the flagship Interactive Flat Panel, with particular focus on the two main use cases – collaboration in meetings and engagement in smart learning.
The new flat panel will help users advance collaboration to a new level, with a more intuitive UI and outstanding imaging. It’s also been designed to be easy on the eye – certified anti-blue light technology1 has been added to reduce the potential damage to the eyes often caused by the blue light emanating from screens.
There’s an AI camera that can track the person who is speaking and acoustic baffle to focus their voice, which makes engagement much higher, especially for those viewing remotely. An intelligent whiteboard provides a smooth writing experience that allows different people to write simultaneously, and various tools to aid presentation and learning. The devices were designed to be as flexible as possible, with multiple projection methods (including wi-fi, software, NFC, and laptop screen mirroring with dongle accessory) and compatibility with various software types (including MS Office, MP4, PDF, and JPG).
The device also offers the ability to enhance administrative efficiency, along with instruction controlling parameter settings, information display, video release, and rapid installation of applications.
All these smart technologies make the Interactive Flat Panel a powerful tool to bring people together in collaboration.
“We live in a world where people need to connect over vast distances to work and learn,” says Henricus Hogenboom – Product Manager of Commercial Display Solutions in Hikvision Europe. “We have noted this and have designed our new Interactive Flat Panel series specifically to make remote collaboration and learning smoother and more engaging. Join us to find out how the new Interactive Flat Panels can revolutionize collaboration and learning in your world.”
Click here to register for the event.
Click here for more information on Hikvision Interactive Flat Panels
1 Certified by TUV Rheinland
SourceHikvision
EMR Analysis
More information on Hikvision: See the full profile on EMR Executive Services
More information on Hu Yangzhong (President & Chief Executive Officer, Hikvision): See the full profile on EMR Executive Services
More information on Henricus Hogenboom (Product Manager, Commercial Display Solutions, Hikvision Europe, Hikvision): See the full profile on EMR Executive Services
More information on TÜV (Technischer Überwachungsverein): https://www.tuv.com/world/en/ + TÜV are internationally active, independent service companies from Germany and Austria that test, inspect and certify technical systems, facilities and objects of all kinds in order to minimize hazards and prevent damages. The TÜV companies are organized into three large holding companies, TÜV Nord, TÜV Rheinland and TÜV SÜD (with TÜV Hessen), along with the smaller independent companies TÜV Thüringen, TÜV Saarland and TÜV Austria.
- TÜV Nord: https://www.tuev-nord-group.com/en/home/ + As a knowledge company, we have our sights firmly set on the digital future. Whether engineers, IT security experts or specialists for the mobility of the future: We ensure that our customers become even more successful in the networked world worldwide.
- More information on Dr. Dirk Stenkamp (Chairman of the Board of Management, TÜV Nord, TÜV): https://www.tuev-nord-group.com/en/company/annual-reports-facts-and-figures/annual-report-2021/the-group-executive-committee/
- TÜV Rheinland: https://www.tuv.com/world/en/ + TÜV Rheinland stands for safety and quality in virtually all areas of business and life. Founded almost 150 years ago, the company is one of the world’s leading testing service providers with more than 20,600 employees and annual revenues of around 2 billion euros. TÜV Rheinland’s highly qualified experts test technical systems and products around the world, support innovations in technology and business, train people in numerous professions and certify management systems according to international standards. In doing so, the independent experts generate trust in products as well as processes across global value-adding chains and the flow of commodities. Since 2006, TÜV Rheinland has been a member of the United Nations Global Compact to promote sustainability and combat corruption.
- More information on Dr.-Ing. Michael Fübi (Chairman of the Board of Management, TÜV Rheinland, TÜV): https://www.tuv.com/world/en/about-us/organisation-and-bodies/profiles/michael-f%C3%BCbi.html +
- TÜV SÜD: https://www.tuvsud.com/de-ch + Digital transformation is already revolutionizing every aspect of our everyday lives. It is changing the way we live, work and spend our free time. In this time of change, TÜV SÜD is committed to creating value for governments, businesses and consumers worldwide. Our goal is to inspire trust in technologies and enable progress by managing technical risks and facilitating change. This commitment is reflected in our new claim “More value. More trust.”
- More information on Dr. Johannes Bussmann (Chairman of the Board of Management, TÜV SÜD, TÜV): https://www.tuvsud.com/de-ch/ueber-uns/leadership
EMR Additional Notes:
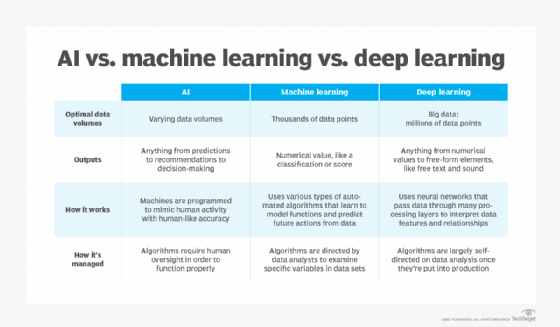
- AI – Artificial Intelligence:
- https://searchenterpriseai.techtarget.com/definition/AI-Artificial-Intelligence +
- Artificial intelligence is the simulation of human intelligence processes by machines, especially computer systems. Specific applications of AI include expert systems, natural language processing, speech recognition and machine vision.
- As the hype around AI has accelerated, vendors have been scrambling to promote how their products and services use AI. Often what they refer to as AI is simply one component of AI, such as machine learning. AI requires a foundation of specialized hardware and software for writing and training machine learning algorithms. No one programming language is synonymous with AI, but a few, including Python, R and Java, are popular.
- In general, AI systems work by ingesting large amounts of labeled training data, analyzing the data for correlations and patterns, and using these patterns to make predictions about future states. In this way, a chatbot that is fed examples of text chats can learn to produce lifelike exchanges with people, or an image recognition tool can learn to identify and describe objects in images by reviewing millions of examples.
- AI programming focuses on three cognitive skills: learning, reasoning and self-correction.
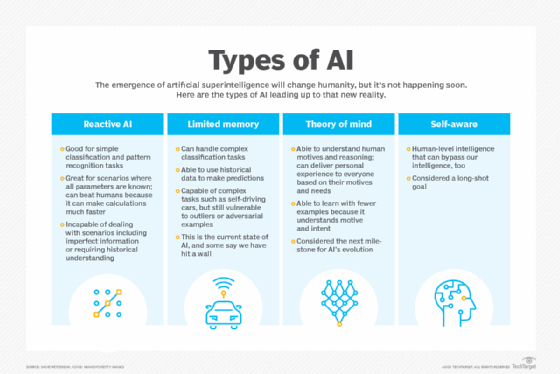
- What are the 4 types of artificial intelligence?
- Type 1: Reactive machines. These AI systems have no memory and are task specific. An example is Deep Blue, the IBM chess program that beat Garry Kasparov in the 1990s. Deep Blue can identify pieces on the chessboard and make predictions, but because it has no memory, it cannot use past experiences to inform future ones.
- Type 2: Limited memory. These AI systems have memory, so they can use past experiences to inform future decisions. Some of the decision-making functions in self-driving cars are designed this way.
- Type 3: Theory of mind. Theory of mind is a psychology term. When applied to AI, it means that the system would have the social intelligence to understand emotions. This type of AI will be able to infer human intentions and predict behavior, a necessary skill for AI systems to become integral members of human teams.
- Type 4: Self-awareness. In this category, AI systems have a sense of self, which gives them consciousness. Machines with self-awareness understand their own current state. This type of AI does not yet exist.
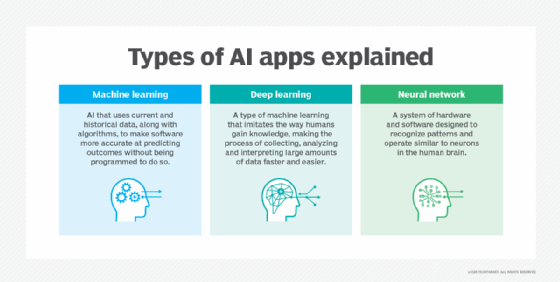
- Machine Learning:
- Developed to mimic human intelligence. It lets the machines learn independently by ingesting vast amounts of data and detecting patterns. Many ML algorithms use statistics formulas and big data to function.
- Type of artificial intelligence (AI) that allows software applications to become more accurate at predicting outcomes without being explicitly programmed to do so. Machine learning algorithms use historical data as input to predict new output values.
- Recommendation engines are a common use case for machine learning. Other popular uses include fraud detection, spam filtering, malware threat detection, business process automation (BPA) and Predictive maintenance.
- Classical machine learning is often categorized by how an algorithm learns to become more accurate in its predictions. There are four basic approaches: supervised learning, unsupervised learning, semi-supervised learning and reinforcement learning. The type of algorithm data scientists choose to use depends on what type of data they want to predict.
- Deep Learning:
- Subset of machine learning. Deep learning enabled much smarter results than were originally possible with machine learning. Consider the face recognition example.
- Deep learning makes use of layers of information processing, each gradually learning more and more complex representations of data. The early layers may learn about colors, the next ones learn about shapes, the following about combinations of those shapes, and finally actual objects. Deep learning demonstrated a breakthrough in object recognition.
- Deep learning is currently the most sophisticated AI architecture we have developed.
- Computer Vision:
- Computer vision is a field of artificial intelligence (AI) that enables computers and systems to derive meaningful information from digital images, videos and other visual inputs — and take actions or make recommendations based on that information.
- The most well-known case of this today is Google’s Translate, which can take an image of anything — from menus to signboards — and convert it into text that the program then translates into the user’s native language.
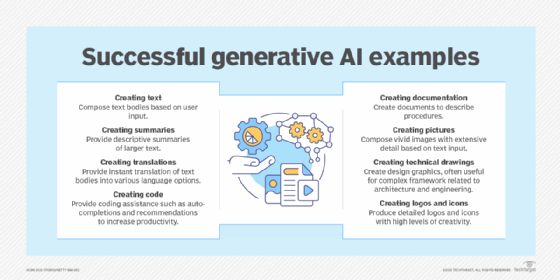
- Generative AI:
- Generative AI technology generates outputs based on some kind of input – often a prompt supplied by a person. Some GenAI tools work in one medium, such as turning text inputs into text outputs, for example. With the public release of ChatGPT in late November 2022, the world at large was introduced to an AI app capable of creating text that sounded more authentic and less artificial than any previous generation of computer-crafted text.
- https://searchenterpriseai.techtarget.com/definition/AI-Artificial-Intelligence +
- Wi-Fi and Z-Wave:
- A Wi-Fi network is simply an internet connection that’s shared with multiple devices in a home or business via a wireless router. The router is connected directly to your internet modem and acts as a hub to broadcast the internet signal to all your Wi-Fi enabled devices.
- Wi-Fi, which most of us are familiar with, operates on either 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz frequencies, providing wireless internet to any connected devices. Z-Wave operates on a much lower frequency — between 800 and 900 MHz — and is primarily for home automation.
- Wi-Fi 2nd Gen: The Standard IEEE 802.11a is referred as WiFi 2. This WiFi Standard is successor to IEEE 802.11b (i.e. WiFi 1). This is the first wifi standard in which multi carrier modulation scheme i.e. OFDM has been introduced to support high data rates unlike single carrier used in wifi-1. The 2.4 GHz frequency of the wifi router offers the wifi user a wide coverage area and is better at penetrating solid objects with a usable speed of 50 -70 Mbps (subject to real world scenarios).
- If you want better range, use 2.4 GHz. If you need higher performance or speed, use the 5GHz band. The 5GHz band, which is the newer of the two, has the potential to cut through network clutter and interference to maximize network performance.
- Z-Wave operates on a completely different wireless frequency that will not conflict with your Wi-Fi network signal. Z-Wave is a mesh technology that strengthens the network with several connected devices. Z-wave is popular as smart-property technology, powering locks, lights, sensors, thermostats, etc.
- Z-wave uses much less power than WiFi. That means that it’s possible to use battery-powered Z-wave devices without worrying about having to change the batteries frequently. Z-wave is also more secure since it’s more of a closed system and can offer some additional layers of protection.
- NFC (Near Field Communication):
- https://nfc-forum.org + standards-based short-range wireless connectivity technology that makes life easier and more convenient for consumers around the world by making it simpler to make transactions, exchange digital content, and connect electronic devices with a touch. NFC is compatible with hundreds of millions of contactless cards and readers already deployed worldwide.
- NFC (Near Field Communication) is the technology behind “tap to pay” contactless payment. Its design conforms to an international standard that features very close proximity (>2cm or one inch) and in most cases does not require a battery “harvesting” it’s power from the connecting device. The NFC Forum is the governing body of the standard and a compliance program that ensures the reliability and interoperability of connections.


