Honeywell – Honeywell Research Indicates Artificial Intelligence Will Shape Global Retail Over The Next 12 Months
Nearly 6 in 10 retailers plan to adopt AI, machine learning and computer vision technologies within the next year
CHARLOTTE, N.C., Aug. 15, 2023 /PRNewswire/ — According to a new survey released today by Honeywell (Nasdaq: HON), nearly six in 10 retailers plan to adopt artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML) and computer vision (CV) technologies over the next year to enhance the shopping experience offered within stores and online. The research also indicates that retailers see this new technology as complementing and enhancing their workforce and not eliminating jobs.
Honeywell’s AI in Retail survey involved some 1,000 retail directors across the United States, Europe, the Middle East and Africa in leadership roles – including IT, operations, and customer experience. Some of the key findings about the state of AI, ML and CV technologies today include:
- 38% of those surveyed are using these technologies for select use cases or regions
- 35% are using them on a larger scale
- 24% are in a pilot phase or in discussions
- Only 3% said they were not using these technologies at all
Nearly half (48%) of respondents identified AI, ML and CV as the top technologies expected to have a significant impact on the retail industry over the next three to five years.
“In today’s retail environment, there is greater attention on the customer experience along with increased need to innovate in a hyper-competitive environment,” said George Koutsaftes, president and CEO of Honeywell Safety and Productivity Solutions. “New technologies like AI, ML and CV have the potential to enable retailers to deliver personalized experiences, optimize operations, improve inventory management and prevent fraud – all of which enhance customer satisfaction and can lead to increased sales and profitability.”
AI to enhance customer experience, efficiencies and more
The convenience of online purchasing with fast delivery and curated in-store shopping options have raised consumers’ expectations. Surveyed retailers said they are highly motivated to implement new technologies that help them achieve their goals. The top three reasons leaders gave for deploying new technologies included:
- Improving customer experience (59%)
- Driving greater productivity (49%)
- Achieving cost efficiencies / return on investment (ROI) (44%)
Survey respondents predict that AI, ML and CV will bring the greatest value to four key functions in retail: automating and supporting day-to-day tasks, such as picking and scheduling; supporting customer service, including live chat, for digital channels; creating targeted customer marketing campaigns and improving inventory management.
AI to complement the future workforce, despite some barriers to adoption
Study findings suggest that most retailers see AI, ML and CV primarily as tools to augment and maximize their workforce, rather than to replace employees. Only 7% of those surveyed said their primary purpose for these solutions would be to reduce human labor. The new technologies can enable better utilization of the workforce through predictive analytics, which can lead, in turn, to improved job satisfaction and more time to focus on higher-value tasks.
Despite the large potential impact of the new technologies – AI, ML and CV – the survey data indicates three primary barriers to widespread adoption:
- Budget restrictions (39%)
- Difficulty in demonstrating business value (29%)
- Lack of internal expertise to maintain the technology (21%)
“The importance of attracting and keeping customers and employees has never been greater,” said Koutsaftes. “As AI continues to evolve, expect an exciting future where innovative technologies unlock new levels of efficiency, engagement and satisfaction in retail.”
For additional information on Honeywell’s solutions for retailers, and to read more about the survey results, please visit: https://sps.honeywell.com/us/en/industries/retail.
Methodology
Honeywell’s AI in Retail online survey of 1,000 Directors in Retail, IT, Operations and Customer Experience was commissioned by Honeywell and conducted by market research company OnePoll, in accordance with the Market Research Society’s code of conduct.
Data was collected between April 3-26, 2023. All participants are double opted in to take part in research and are paid an amount depending on the length and complexity of the survey. This survey was overseen and edited by the OnePoll research team. OnePoll are MRS Company Partners, corporate membership of ESOMAR and Members of the British Polling Council.
SourceHoneywell
EMR Analysis
More information on Honeywell: See the full profile on EMR Executive Services
More information on Vimal Kapur (CEO, Honeywell): See the full profile on EMR Executive Services
More information on Honeywell Safety and Productivity Solutions (SPS): https://sps.honeywell.com/us/en + Honeywell Safety and Productivity Solutions (SPS) provides products, software and connected solutions that improve productivity, workplace safety and asset performance for our customers across the globe. We deliver on this promise through industry-leading mobile devices, software, cloud technology and automation solutions, a broad range of personal protective equipment and gas detection technology, and custom-engineered sensors, switches and controls.
More information on George Koutsaftes (President and CEO, Honeywell Safety and Productivity Solutions (SPS)): See the full profile on EMR Executive Services
More information on OnePoll: https://onepoll.com/ + Powering online market research and PR surveys with global human experiences.
EMR Additional Notes:
- AI – Artificial Intelligence:
- https://searchenterpriseai.techtarget.com/definition/AI-Artificial-Intelligence +
- Artificial intelligence is the simulation of human intelligence processes by machines, especially computer systems. Specific applications of AI include expert systems, natural language processing, speech recognition and machine vision.
- As the hype around AI has accelerated, vendors have been scrambling to promote how their products and services use AI. Often what they refer to as AI is simply one component of AI, such as machine learning. AI requires a foundation of specialized hardware and software for writing and training machine learning algorithms. No one programming language is synonymous with AI, but a few, including Python, R and Java, are popular.
- In general, AI systems work by ingesting large amounts of labeled training data, analyzing the data for correlations and patterns, and using these patterns to make predictions about future states. In this way, a chatbot that is fed examples of text chats can learn to produce lifelike exchanges with people, or an image recognition tool can learn to identify and describe objects in images by reviewing millions of examples.
- AI programming focuses on three cognitive skills: learning, reasoning and self-correction.
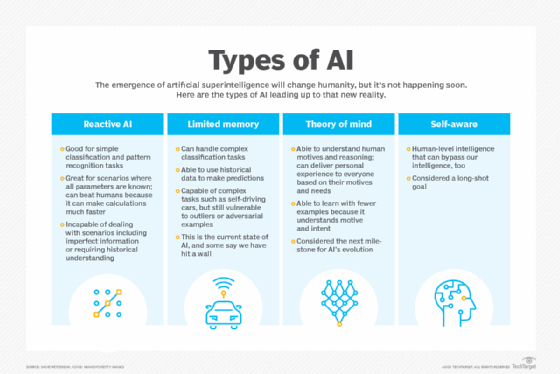
- What are the 4 types of artificial intelligence?
- Type 1: Reactive machines. These AI systems have no memory and are task specific. An example is Deep Blue, the IBM chess program that beat Garry Kasparov in the 1990s. Deep Blue can identify pieces on the chessboard and make predictions, but because it has no memory, it cannot use past experiences to inform future ones.
- Type 2: Limited memory. These AI systems have memory, so they can use past experiences to inform future decisions. Some of the decision-making functions in self-driving cars are designed this way.
- Type 3: Theory of mind. Theory of mind is a psychology term. When applied to AI, it means that the system would have the social intelligence to understand emotions. This type of AI will be able to infer human intentions and predict behavior, a necessary skill for AI systems to become integral members of human teams.
- Type 4: Self-awareness. In this category, AI systems have a sense of self, which gives them consciousness. Machines with self-awareness understand their own current state. This type of AI does not yet exist.
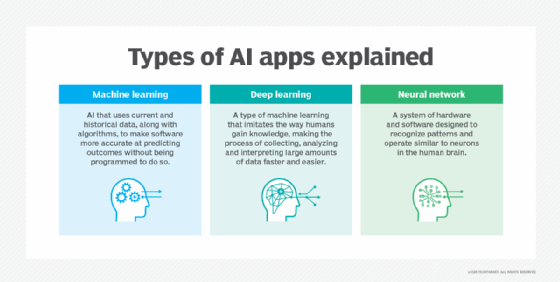
- Machine Learning:
- Developed to mimic human intelligence. It lets the machines learn independently by ingesting vast amounts of data and detecting patterns. Many ML algorithms use statistics formulas and big data to function.
- Type of artificial intelligence (AI) that allows software applications to become more accurate at predicting outcomes without being explicitly programmed to do so. Machine learning algorithms use historical data as input to predict new output values.
- Recommendation engines are a common use case for machine learning. Other popular uses include fraud detection, spam filtering, malware threat detection, business process automation (BPA) and Predictive maintenance.
- Classical machine learning is often categorized by how an algorithm learns to become more accurate in its predictions. There are four basic approaches:supervised learning, unsupervised learning, semi-supervised learning and reinforcement learning. The type of algorithm data scientists choose to use depends on what type of data they want to predict.
- Deep Learning:
- Subset of machine learning. Deep learning enabled much smarter results than were originally possible with machine learning. Consider the face recognition example.
- Deep learning makes use of layers of information processing, each gradually learning more and more complex representations of data. The early layers may learn about colors, the next ones learn about shapes, the following about combinations of those shapes, and finally actual objects. Deep learning demonstrated a breakthrough in object recognition.
- Deep learning is currently the most sophisticated AI architecture we have developed.
- Computer Vision:
- Computer vision is a field of artificial intelligence (AI) that enables computers and systems to derive meaningful information from digital images, videos and other visual inputs — and take actions or make recommendations based on that information.
- The most well-known case of this today is Google’s Translate, which can take an image of anything — from menus to signboards — and convert it into text that the program then translates into the user’s native language.
- https://searchenterpriseai.techtarget.com/definition/AI-Artificial-Intelligence +