LEDVANCE – LEDVANCE presents “LEDVANCE LOOP” laying the foundation for more sustainability in the lighting industry
“From line to loop”: new LEDVANCE LOOP brand bundles the lighting experts’ sustainability endeavors
LEDVANCE increases its efforts to transform the lighting industry into a greener one. With the new “LEDVANCE LOOP”, the lighting experts introduce a sub-brand for all their sustainability efforts and measures across the company. This includes new product ranges, reducing CO2 levels by a million tons annually in transportation and improving demand planning with AI. Additionally, LEDVANCE will relocate its headquarters and reduce the size of its office space in order to operate more efficiently and also better reflect its flexible home office policy. The new optimized headquarters will also be named “LEDVANCE LOOP” to demonstrate the company’s commitment to sustainability in everyday operations.

Gareth Jackson
The concept behind the LEDVANCE LOOP brand is a big step for the company and is expected to transform the future of the lighting industry:
“We invested millions of dollars into research and development so that we can contribute to a more sustainable industry,” says Gareth Jackson, Chief Operating Officer at LEDVANCE. “In this era of transformation at LEDVANCE, sustainability is not a destination but a continuous journey. It’s about more than just being environmentally conscious; it’s about reshaping our practices, reducing our carbon footprint, creating collaborative spaces, and promoting ethical business conduct. As we evolve, we’re not only enhancing our competitiveness but also nurturing a sustainable future for our business, the environment, and our people. It’s our pledge to do better today than we did yesterday and to inspire others to join us on this path. This is what LEDVANCE LOOP stands for.”
In addition to the numerous activities that will transform the company itself, LEDVANCE will soon launch two new product ranges under the LEDVANCE LOOP umbrella:
- EVERLOOP is a range of innovative products that enable professional customers to replace certain components of a luminaire, thereby increasing the lifespan of a product and reducing waste.
- NATURELOOP, a product line catering to end-consumers, will offer products that are made from recycled materials.
More information regarding the new product ranges EVERLOOP and NATURELOOP will be announced soon.
SourceLEDVANCE
EMR Analysis
More information on LEDVANCE: https://www.ledvance.com + With subsidiaries in more than 50 countries and business activities in over 140 countries, LEDVANCE is one of the world’s leading companies in the field of general lighting for professional customers and end users. Emerging from OSRAM’s general lighting division, LEDVANCE’s portfolio includes a wide range of LED luminaires for a variety of applications, intelligent lighting products for smart homes and smart buildings, one of the most comprehensive offerings of advanced LED lamps in the lighting industry, and traditional lamps. In addition to offering products under its own product brand LEDVANCE, the company continues to use the OSRAM and SYLVANIA trademarks for many of its products in agreement with OSRAM. Beyond lighting, LEDVANCE offers vertically integrated, renewable energy solutions for the building sector. Together, the lighting division and the renewable energy division form a comprehensive ecosystem for residential, commercial and industrial buildings.
To reflect our broad range of products and solutions, we offer a variety of brands under our LEDVANCE corporate umbrella. Under the LEDVANCE product brand, we sell an extensive line of products for residential, commercial and industrial applications. In agreement with OSRAM, we also sell a large selection of products under the OSRAM and SYLVANIA product brands. In addition to this, we have a plethora of brands for our owned technologies and features, like our light management system VIVARES, PHASE EV™ charging infrastructure as well as our BIOLUX Human Centric Lighting system.
After spinning off from OSRAM in 2016, the company is now owned by Chinese lighting enterprise MLS Co., LTD.

More information on Sun Qinghuan (President, MLS + CEO and Managing Director, LEDVANCE): See the full profile on EMR Executive Services
More information on Chu Shi-Ting (Managing Director, LEDVANCE): See the full profile on EMR Executive Services
More information on Bart Mei (Chief Sales & Marketing Officer, LEDVANCE): See the full profile on EMR Executive Services
More information on Gareth Jackson (Chief Operating Officer, LEDVANCE): See the full profile on EMR Executive Services
More information on Vivian Lee-Lauss (Head of Global Brand Management, LEDVANCE): See the full profile on EMR Executive Services
More information on “LEDVANCE LOOP” by LEDVANCE:
- Sub-brand for all LEDVANCE sustainability efforts and measures across the company. This includes new product ranges, reducing CO2 levels by a million tons annually in transportation and improving demand planning with AI.
- Under the LEDVANCE LOOP umbrella, two new product ranges will be launched:
- EVERLOOP is a range of innovative products that enable professional customers to replace certain components of a luminaire, thereby increasing the lifespan of a product and reducing waste.
- NATURELOOP, a product line catering to end-consumers, will offer products that are made from recycled materials.
- Under the LEDVANCE LOOP umbrella, two new product ranges will be launched:
- “LEDVANCE LOOP” will also be the name of the new optimized headquarters of LEDVANCE.
- Sustainability is not a destination but a continuous journey. It’s about more than just being environmentally conscious; it’s about reshaping our practices, reducing our carbon footprint, creating collaborative spaces, and promoting ethical business conduct. As we evolve, we’re not only enhancing our competitiveness but also nurturing a sustainable future for our business, the environment, and our people. It’s our pledge to do better today than we did yesterday and to inspire others to join us on this path. This is what LEDVANCE LOOP stands for.
EMR Additional Notes:
- AI – Artificial Intelligence:
- https://searchenterpriseai.techtarget.com/definition/AI-Artificial-Intelligence +
- Artificial intelligence is the simulation of human intelligence processes by machines, especially computer systems. Specific applications of AI include expert systems, natural language processing, speech recognition and machine vision.
- As the hype around AI has accelerated, vendors have been scrambling to promote how their products and services use AI. Often what they refer to as AI is simply one component of AI, such as machine learning. AI requires a foundation of specialized hardware and software for writing and training machine learning algorithms. No one programming language is synonymous with AI, but a few, including Python, R and Java, are popular.
- In general, AI systems work by ingesting large amounts of labeled training data, analyzing the data for correlations and patterns, and using these patterns to make predictions about future states. In this way, a chatbot that is fed examples of text chats can learn to produce lifelike exchanges with people, or an image recognition tool can learn to identify and describe objects in images by reviewing millions of examples.
- AI programming focuses on three cognitive skills: learning, reasoning and self-correction.
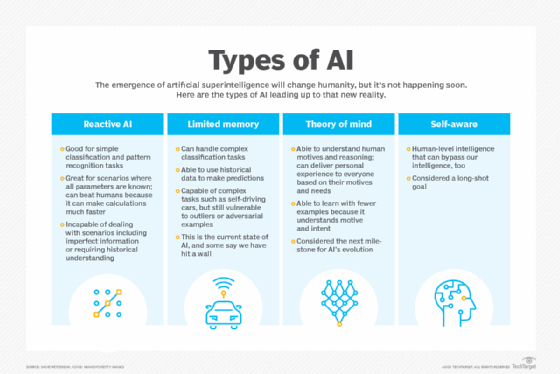
- What are the 4 types of artificial intelligence?
- Type 1: Reactive machines. These AI systems have no memory and are task specific. An example is Deep Blue, the IBM chess program that beat Garry Kasparov in the 1990s. Deep Blue can identify pieces on the chessboard and make predictions, but because it has no memory, it cannot use past experiences to inform future ones.
- Type 2: Limited memory. These AI systems have memory, so they can use past experiences to inform future decisions. Some of the decision-making functions in self-driving cars are designed this way.
- Type 3: Theory of mind. Theory of mind is a psychology term. When applied to AI, it means that the system would have the social intelligence to understand emotions. This type of AI will be able to infer human intentions and predict behavior, a necessary skill for AI systems to become integral members of human teams.
- Type 4: Self-awareness. In this category, AI systems have a sense of self, which gives them consciousness. Machines with self-awareness understand their own current state. This type of AI does not yet exist.
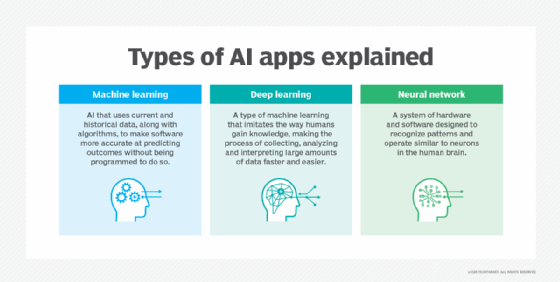
- Machine Learning:
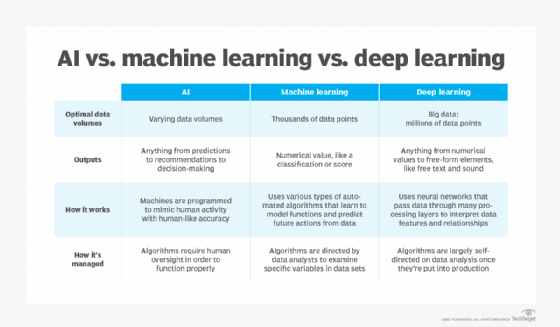
- Developed to mimic human intelligence. It lets the machines learn independently by ingesting vast amounts of data and detecting patterns. Many ML algorithms use statistics formulas and big data to function.
- Type of artificial intelligence (AI) that allows software applications to become more accurate at predicting outcomes without being explicitly programmed to do so. Machine learning algorithms use historical data as input to predict new output values.
- Recommendation engines are a common use case for machine learning. Other popular uses include fraud detection, spam filtering, malware threat detection, business process automation (BPA) and Predictive maintenance.
- Classical machine learning is often categorized by how an algorithm learns to become more accurate in its predictions. There are four basic approaches:supervised learning, unsupervised learning, semi-supervised learning and reinforcement learning. The type of algorithm data scientists choose to use depends on what type of data they want to predict.
- Deep Learning:
- Subset of machine learning. Deep learning enabled much smarter results than were originally possible with machine learning. Consider the face recognition example.
- Deep learning makes use of layers of information processing, each gradually learning more and more complex representations of data. The early layers may learn about colors, the next ones learn about shapes, the following about combinations of those shapes, and finally actual objects. Deep learning demonstrated a breakthrough in object recognition.
- Deep learning is currently the most sophisticated AI architecture we have developed.
- Computer Vision:
- Computer vision is a field of artificial intelligence (AI) that enables computers and systems to derive meaningful information from digital images, videos and other visual inputs — and take actions or make recommendations based on that information.
- The most well-known case of this today is Google’s Translate, which can take an image of anything — from menus to signboards — and convert it into text that the program then translates into the user’s native language.
- https://searchenterpriseai.techtarget.com/definition/AI-Artificial-Intelligence +
- Carbon Dioxide (CO2):
- Primary greenhouse gas emitted through human activities. Carbon dioxide enters the atmosphere through burning fossil fuels (coal, natural gas, and oil), solid waste, trees and other biological materials, and also as a result of certain chemical reactions (e.g., manufacture of cement). Carbon dioxide is removed from the atmosphere (or “sequestered”) when it is absorbed by plants as part of the biological carbon cycle.
- Decarbonization:
- Reduction of carbon dioxide emissions through the use of low carbon power sources, achieving a lower output of greenhouse gasses into the atmosphere.


