Prysmian – Prysmian to enhance its digital solutions business with the acquisition of Channell
- PRYSMIAN WILL STRENGTHEN ITS DIGITAL SOLUTIONS BUSINESS VIA THE ACQUISITION OF A MARKET-LEADING CONNECTIVITY PLAYER WITH A 100+ YEAR OPERATING HISTORY IN THE UNITED STATES
- CHANNELL REPRESENTS PRYSMIAN’S FIRST MAJOR ACQUISITION IN DIGITAL SOLUTIONS AND WILL ACCELERATE ITS JOURNEY FROM CABLE MANUFACTURER TO SOLUTIONS PROVIDER
- PRYSMIAN EXPECTS TO BENEFIT FROM CHANNELL’S EXPANSIVE COMMERCIAL REACH, BROAD PRODUCT PORTFOLIO AND STRONG CULTURE OF INNOVATION DRIVEN BY THE DEEP EXPERTISE OF CHANNELL’S EMPLOYEE BASE
- CHANNELL’S CONNECTIVITY SOLUTIONS WILL COMPLEMENT PRYSMIAN’S EXISTING FIBER OPTIC PRODUCTION AND SYNERGISTIC PORTFOLIO, INCLUDING ENERGY SOLUTIONS
- THE ACQUISITION IS FOR A TOTAL OF $950 MILLION, PLUS A POTENTIAL EARN-OUT OF UP TO $200 MILLION
Prysmian has agreed to acquire Channell Commercial Corporation (“Channell”), a leading connectivity solutions provider in the United States, for a total consideration of $950 million, subject to certain closing adjustments, and for a potential additional post-closing payment of up to $200 million based on Channell’s achievement of certain EBITDA targets for calendar year 2025. The transaction value represents a multiple of less than 8.0x 2024A EBITDA. The transaction is subject to customary closing conditions, including regulatory clearances, and is expected to close in the second quarter of 2025.
The acquisition will be funded by a balanced mix of debt and equity capital market instruments, including hybrid bonds and treasury shares disposal.
The acquisition, Prysmian’s first major Digital Solutions transaction, will accelerate its journey from cable manufacturer to solutions provider. The combined portfolio of Prysmian and Channell solutions, along with Channell’s extended commercial reach and complementary R&D focus, will support the development of Prysmian’s North American footprint, positioning the business for the growth of data centres and the roll-out of FTTX and 5G in the United States and Europe. Channell will be included in Prysmian’s Digital Solutions, which is part of its broader synergistic portfolio, including energy solutions.
Massimo Battaini, Prysmian CEO, said: “Our journey from cable manufacturer to world class solutions provider is accelerating, and thanks to strengthening in the connectivity solutions space, we will be best placed to capture growth in the market, which is being boosted by digitalisation and the roll-out of AI. We are strengthening our exposure to North America, while at the same time gaining know-how and a product portfolio which will enable us to be even more competitive across the globe. Channell are renowned for their excellence and share a spirit of innovation with Prysmian as we both offer best-in-class quality solutions that act as a driver for growth. I would like to thank CEO and owner Bill Channell Jr for entrusting Prysmian with Channell’s next step. For generations, he and his family have built a market-leader and an outstanding culture of innovation, and together with our fiber optic cables and portfolio of energy solutions, we will offer customers a true one-stop-shop, while creating value for all stakeholders.”
Channell is headquartered in Rockwall, Texas and has just under 1,000 employees. Founded in 1922 by the Channell family, Channell is an established connectivity player in the United States with three manufacturing facilities in Texas, Nevada and California. Prysmian expects Channell to complement Prysmian’s current Digital Solutions business thanks to Channell’s vertical integration philosophy, US manufacturing and commercial footprint, and diverse product portfolio of vaults, fiber optics, thermoplastic enclosures and metal enclosures. Channell’s broad customer base includes leading operators across the Telecommunications, Broadband, Utility and Power sectors.
Bill Channell Jr, Channell CEO and owner, said: “Today is an incredibly exciting day for Channell. I am confident that Prysmian is the right strategic partner to drive the next phase of growth for Channell. I know that Massimo and his team share in the vision that together, our two companies can accomplish more, and I am truly excited about the benefits the combination brings to Channell’s customers and employees. I want to thank the best-in-class employees, past and present, who have been part of the Channell family since Channell was founded over 100 years ago by my grandfather; you are, and have been, the driving force behind Channell’s success. Massimo and his team, together with myself and Channell President Chris Watson, will work toward combining the best of what our companies do well to expand Prysmian’s capabilities as a Digital Solutions provider. I believe strongly that Prysmian is the best new home for Channell and its employees and will safeguard the Channell legacy for the next 100 years.”
SourcePrysmian
EMR Analysis
More information on Prysmian: See the full profile on EMR Executive Services
More information on Massimo Battaini (Group Chief Executive Officer and General Manager, Prysmian Group): See the full profile on EMR Executive Services
More information on Pier Francesco Facchini (Chief Financial Officer and Executive Director, Finance, Administration, Control and IT, Prysmian): See the full profile on EMR Executive Services
More information on Lars Frederick Persson (Executive Vice President, Digital Solutions Business, Prysmian Group + Chairman of the Cable and Insulated Wire Association, ZVEI): See the full profile on EMR Executive Services
More information on Andrea Pirondini (Chief Executive Officer, North America, Executive Director, Prysmian Group): See the full profile on EMR Executive Services
More information on Channell Commercial Corporation by Prysmian: https://www.channell.com/ + Channell Commercial Corporation is a proud United States Manufacturer, and global supplier of world-class fiber optic solutions, thermoplastic pedestals, and grade level vaults for all your outside plant construction needs. We specialize in end-to-end, full network solutions, and have been at the forefront of industry innovation for over ninety years. We continue to evolve our products to best serve the ever-changing needs and demands of outside plant construction.
Since 1922, we have invented, designed, patented, and manufactured our products proudly in the United States. Today we produce tools, dies, and molds for all of our manufacturing platforms to provide true end-to-end innovation. Our facilities today feature high automation robotics and true end-to-end material processing. By maintaining control over the complete process we can assure that every product we produce is unmatched in quality, structural integrity, and design.
Channell is headquartered in Rockwall, Texas and has just under 1,000 employees. Founded in 1922 by the Channell family, Channell is an established connectivity player in the United States with three manufacturing facilities in Texas, Nevada and California.
Channell’s broad customer base includes leading operators across the Telecommunications, Broadband, Utility and Power sectors.
More information on William H. Channell Jr (Owner and Chief Executive Officer, Channell, Prysmian): See the full profile on EMR Executive Services
More information on Chris Watson (President, Channell, Prysmian): N.A.
EMR Additional Notes:
- EBITA:
- Earnings before interest, taxes, and amortization (EBITA) is a measure of company profitability used by investors. It is helpful for comparing one company to another in the same line of business.
- EBITA = Net income + Interest + Taxes + Amortization
- EBITDA:
- Earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA) is an alternate measure of profitability to net income. By including depreciation and amortization as well as taxes and debt payment costs, EBITDA attempts to represent the cash profit generated by the company’s operations.
- EBITDA and EBITA are both measures of profitability. The difference is that EBITDA also excludes depreciation.
- EBITDA is the more commonly used measure because it adds depreciation—the accounting practice of recording the reduced value of a company’s tangible assets over time—to the list of factors.
- EV/EBITDA (Enterprise Multiple):
- Enterprise multiple, also known as the EV-to-EBITDA multiple, is a ratio used to determine the value of a company.
- It is computed by dividing enterprise value by EBITDA.
- The enterprise multiple takes into account a company’s debt and cash levels in addition to its stock price and relates that value to the firm’s cash profitability.
- Enterprise multiples can vary depending on the industry.
- Higher enterprise multiples are expected in high-growth industries and lower multiples in industries with slow growth.
- Bonds:
- Bonds are issued by governments and corporations when they want to raise money. By buying a bond, you’re giving the issuer a loan, and they agree to pay you back the face value of the loan on a specific date, and to pay you periodic interest payments along the way, usually twice a year.
- In simple terms, a bond is loan from an investor to a borrower such as a company or government. The borrower uses the money to fund its operations, and the investor receives interest on the investment. The market value of a bond can change over time.
- Green Bonds:
- Green Bonds enable capital-raising and investment for new and existing projects with environmental benefits. The Green Bond Principles (GBP) seek to support issuers in financing environmentally sound and sustainable projects that foster a net-zero emissions economy and protect the environment.
- Blue Bonds:
- The World Bank defines blue bonds “as a debt instrument issued by governments, development banks or others to raise capital from impact investors to finance marine and ocean-based projects that have positive environmental, economic and climate benefits.”
- Blue bonds work in the same way than traditional bonds but are different in that the entities issuing them are determined to use the resources generated – or a large proportion thereof – for the protection and conservation of marine ecosystems.
- Green vs. Blue Bonds:
- Projects eligible for green bond financing may include all eligible renewable energy projects, and projects eligible for blue bond financing may only include renewable energy projects that focus on marine and offshore renewable energy.
- Broadband Connectivity:
- Broadband refers to various high-capacity transmission technologies that transmit data, voice, and video across long distances and at high speeds.
- Broadband refers to telecommunications in which a wide band of frequencies is available to transmit information. Because a wide band of frequencies is available, information can be multiplexed and sent on many different frequencies or channels within the band concurrently. Multiplexing enables more information to be transmitted in a given time, much as more lanes on a highway support more cars.
- Optical Cabling:
- An optical cable transfers audio digitally, but instead of copper wire, light is used. This is a variation of fiber optics, which is used in a variety of applications.
- The biggest difference between Optical Cables and HDMI is that HDMI can pass higher-resolution audio, including the formats found on Blu-ray: Dolby TrueHD and DTS HD Master Audio. These formats can’t get transmitted across optical. In terms of simplicity, HDMI also passes video signals.
- Network Cabling:
- Coaxial Cable:
- Coaxial cables or coax, have a single copper conductor at the center, while a plastic layer provides insulation between the center conductor and braided metal shield. The metal shield blocks outside interference from fluorescent lights, motors, and other computers.
- Twisted Pair:
- Twisted pair uses copper wires that are, as the name suggests, twisted together in pairs. The twist effect of each pair in the cables ensures any interference presented or picked up on one cable is canceled by the cable’s partner that twists around the initial cable. Twisting the two wires also reduces the electromagnetic radiation emitted by the circuit.
- Shielded Twisted Pair (STP) Cable:
- In STP, copper wires are first covered by plastic insulation. A metal shield, which consists of metal foil or braid, surrounds the bundle of insulated pairs. Where electromagnetic radiation is a serious issue, each pair of wires may be individually shielded in addition to the outer shield. This is known as foil twisted pair (FTP).
- Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP) Cable:
- UTP cables typically contain four pairs of copper wires, with each pair containing two wires twisted together. These pairs are covered by plastic insulation. They do not have any shielding and just have an outer jacket.
- Most categories of twisted-pair cables are available as UTP. But some newer categories are also available in combinations of shielded, foil shielded and unshielded.
- Shielded Twisted Pair (STP) Cable:
- Twisted pair uses copper wires that are, as the name suggests, twisted together in pairs. The twist effect of each pair in the cables ensures any interference presented or picked up on one cable is canceled by the cable’s partner that twists around the initial cable. Twisting the two wires also reduces the electromagnetic radiation emitted by the circuit.
- Fiber Optic Cable:
- Fiber optic cables consist of a thin optical fiber surrounded by cladding. Cladding is made from glass that is less pure than the core and has a lower refractive index than the core. The difference in refractive indices causes light to be reflected at the boundary. Additional layers, such as the buffer layer and jacket layer, surround the cladding to add strength and protect the cable against damage.
- Data rates have increased throughout the network, and in some cases, fiber optics is the only option. While Cat8 twisted-pair cables can carry up to 40 Gbps of data, fiber supports data rates up to 400 Gbps.
- Fiber has a low error rate. Network data is encoded in a light beam. Unlike with twisted-pair cables, the light beam neither generates nor is affected by electronic interference. Additionally, multiple frequency data streams can be multiplexed over a single fiber to increase the total data rate.
- Coaxial Cable:

- FTTx:
- Fiber to the Home (FTTH), Fiber to the Building (FTTB), Fiber to the Premises (FTTP) and Fiber to the Curb (FTTC), termed as FTTx are various technology and deployment options developed to enable reach of fiber as close to the user location as possible to provide high speed data and voice services.
- Fiber to the home (FTTH) is the delivery of a communications signal over optical fiber from the operator’s switching equipment all the way to a home or business, thereby replacing existing copper infrastructure such as telephone wires and coaxial cable.
- FTTP and FTTH are two different abbreviations for the same thing. FTTP stands for ‘fibre to the premises’ and FTTH stands for ‘fibre to the home’. … Unlike FTTC, FTTP broadband is delivered via fibre-optic cables not only as far as the cabinet, but across the entire span to your home or business.
- Fiber-optic cables are less susceptible to glitches than traditional copper wires and can withstand the shock and vibration from inclement weather. FTTH is considered “future proof” and offers the flexibility to deliver additional services in the years to come.

- Key Differences Between Copper Cable and Fiber Optics:
- Data transmission speed of a fiber cable is comparatively more than that of copper cable. Copper cables are nearly 31% slower in data transmission than fiber cable.
- A copper cable transmits the data through it in the form of electrical pulse i.e., due to the movement of electrons. As against in a fiber optics, the data transmission is the result of movement of photons thus it transmits in the form of light pulses.
- The bandwidth provided by a copper cable is less than that of the fiber optics. Thus, a copper cabling meets the industry standards and provides a performance of up to 10 Gbps. However, a fiber optics due to its large bandwidth possess better performance of up to 60 Tbps and above.
- The energy consumed by a copper cable during its operation is somewhat greater than 10W but on the other side, fiber optics consumes less energy i.e., around 2W per user.
- The lifespan of a copper wire is approximately 5 years as it gets easily affected by temperature variations and other environmental factors. However, fiber optics possess a lifespan of 30 to 50 years.
- As fiber optics are difficult to be tapped as compared to copper cables thus proves advantageous from the security point of view. Due to this reason fiber optics are widely used for data transmission at present time.
- A fiber optics allows transmission of data at a much faster rate as compared to copper cable.
- The installation and maintenance cost of a fiber cable is more than copper cable.
- 4G, 5G and 6G:
- 5G enables a new kind of network that is designed to connect virtually everyone and everything together including machines, objects, and devices.
- First generation – 1G
1980s: 1G delivered analog voice. - Second generation – 2G
Early 1990s: 2G introduced digital voice (e.g. CDMA- Code Division Multiple Access). - Third generation – 3G
Early 2000s: 3G brought mobile data (e.g. CDMA2000). - Fourth generation – 4G LTE
2010s: 4G LTE ushered in the era of mobile broadband.
- First generation – 1G
- 5G has started hitting the market end of 2018 and will continue to expand worldwide unleashing also a massive 5G IoT (Internet of Things) ecosystem.
- 5G speed tops out at 10 gigabits per second (Gbps).
- 5G is 10 to x100 faster than what you can get with 4G.
- The main evolution compared with today’s 4G and 4.5G (aka LTE advanced, LTE-A, LTE+ or 4G+) is that, beyond data speed improvements, new IoT and critical communication use cases will require a new level of improved performance.
- For example, low latency provides real-time interactivity for services using the cloud: this is key to the success of self-driving cars, for example.
- 5G vs 4G also means at least x100 devices connected. 5G must be able to support 1 million devices for 0.386 square miles or 1 km2.
- Also, low power consumption is what will allow connected objects to operate for months or years without the need for human assistance.
- Unlike current IoT services that make performance trade-offs to get the best from current wireless technologies (3G, 4G, Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, Zigbee, etc.), 5G networks will be designed to bring the level of performance needed for massive IoT.
- 6G (sixth-generation wireless) is the successor to 5G cellular technology. 6G networks will be able to use higher frequencies than 5G networks and provide substantially higher capacity and much lower latency. One of the goals of the 6G internet is to support one microsecond latency communications. This is 1,000 times faster — or 1/1000th the latency — than one millisecond throughput.
- The 6G technology market is expected to facilitate large improvements in the areas of imaging, presence technology and location awareness. Working in conjunction with artificial intelligence (AI), the 6G computational infrastructure will be able to identify the best place for computing to occur; this includes decisions about data storage, processing and sharing.
- It is important to note that 6G is not yet a functioning technology. While some vendors are investing in the next-generation wireless standard, industry specifications for 6G-enabled network products remain years away. 6G internet is expected to launch commercially in 2030.
- 5G enables a new kind of network that is designed to connect virtually everyone and everything together including machines, objects, and devices.
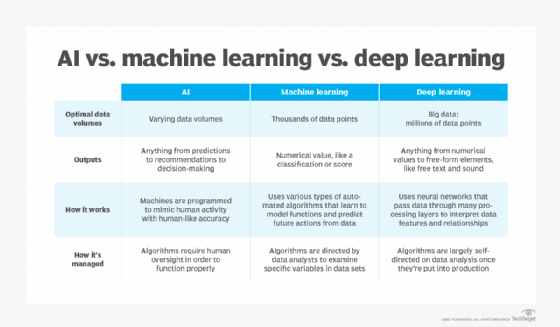
- AI – Artificial Intelligence:
- Artificial intelligence is the simulation of human intelligence processes by machines, especially computer systems.
- As the hype around AI has accelerated, vendors have been scrambling to promote how their products and services use AI. Often what they refer to as AI is simply one component of AI, such as machine learning. AI requires a foundation of specialized hardware and software for writing and training machine learning algorithms. No one programming language is synonymous with AI, but well a few, including Python, R and Java, are popular.
- In general, AI systems work by ingesting large amounts of labeled training data, analyzing the data for correlations and patterns, and using these patterns to make predictions about future states. In this way, a chatbot that is fed examples of text chats can learn to produce lifelike exchanges with people, or an image recognition tool can learn to identify and describe objects in images by reviewing millions of examples.
- AI programming focuses on three cognitive skills: learning, reasoning and self-correction.
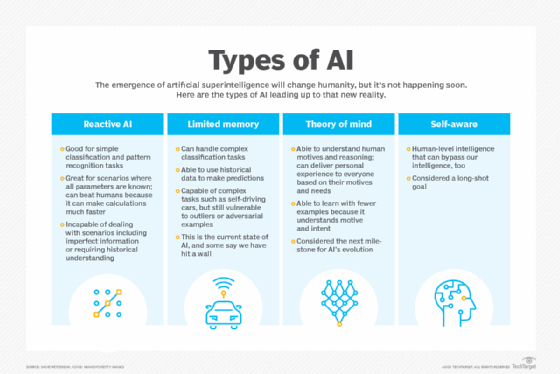
- What are the 4 types of artificial intelligence?
- Type 1: Reactive machines. These AI systems have no memory and are task specific. An example is Deep Blue, the IBM chess program that beat Garry Kasparov in the 1990s. Deep Blue can identify pieces on the chessboard and make predictions, but because it has no memory, it cannot use past experiences to inform future ones.
- Type 2: Limited memory. These AI systems have memory, so they can use past experiences to inform future decisions. Some of the decision-making functions in self-driving cars are designed this way.
- Type 3: Theory of mind. Theory of mind is a psychology term. When applied to AI, it means that the system would have the social intelligence to understand emotions. This type of AI will be able to infer human intentions and predict behavior, a necessary skill for AI systems to become integral members of human teams.
- Type 4: Self-awareness. In this category, AI systems have a sense of self, which gives them consciousness. Machines with self-awareness understand their own current state. This type of AI does not yet exist.
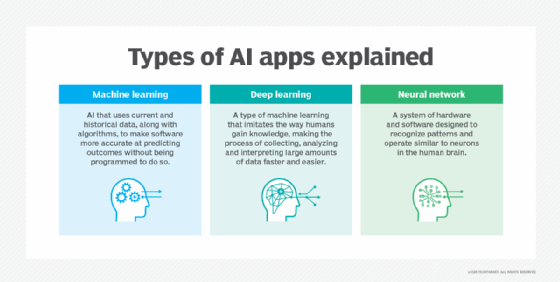
- Machine Learning (ML):
- Developed to mimic human intelligence, it lets the machines learn independently by ingesting vast amounts of data, statistics formulas and detecting patterns.
- ML allows software applications to become more accurate at predicting outcomes without being explicitly programmed to do so.
- ML algorithms use historical data as input to predict new output values.
- Recommendation engines are a common use case for ML. Other uses include fraud detection, spam filtering, business process automation (BPA) and predictive maintenance.
- Classical ML is often categorized by how an algorithm learns to become more accurate in its predictions. There are four basic approaches: supervised learning, unsupervised learning, semi-supervised learning and reinforcement learning.
- Deep Learning (DL):
- Subset of machine learning, Deep Learning enabled much smarter results than were originally possible with ML. Face recognition is a good example.
- DL makes use of layers of information processing, each gradually learning more and more complex representations of data. The early layers may learn about colors, the next ones about shapes, the following about combinations of those shapes, and finally actual objects. DL demonstrated a breakthrough in object recognition.
- DL is currently the most sophisticated AI architecture we have developed.
- Computer Vision (CV):
- Computer vision is a field of artificial intelligence that enables computers and systems to derive meaningful information from digital images, videos and other visual inputs — and take actions or make recommendations based on that information.
- The most well-known case of this today is Google’s Translate, which can take an image of anything — from menus to signboards — and convert it into text that the program then translates into the user’s native language.
- Machine Vision (MV):
- Machine Vision is the ability of a computer to see; it employs one or more video cameras, analog-to-digital conversion and digital signal processing. The resulting data goes to a computer or robot controller. Machine Vision is similar in complexity to Voice Recognition.
- MV uses the latest AI technologies to give industrial equipment the ability to see and analyze tasks in smart manufacturing, quality control, and worker safety.
- Computer Vision systems can gain valuable information from images, videos, and other visuals, whereas Machine Vision systems rely on the image captured by the system’s camera. Another difference is that Computer Vision systems are commonly used to extract and use as much data as possible about an object.
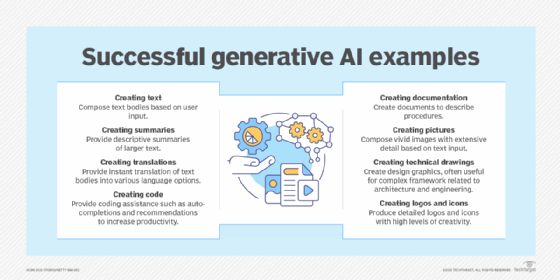
- Generative AI (GenAI):
- Generative AI technology generates outputs based on some kind of input – often a prompt supplied by a person. Some GenAI tools work in one medium, such as turning text inputs into text outputs, for example. With the public release of ChatGPT in late November 2022, the world at large was introduced to an AI app capable of creating text that sounded more authentic and less artificial than any previous generation of computer-crafted text.
- Edge AI Technology:
- Edge artificial intelligence refers to the deployment of AI algorithms and AI models directly on local edge devices such as sensors or Internet of Things (IoT) devices, which enables real-time data processing and analysis without constant reliance on cloud infrastructure.
- Simply stated, edge AI, or “AI on the edge“, refers to the combination of edge computing and artificial intelligence to execute machine learning tasks directly on interconnected edge devices. Edge computing allows for data to be stored close to the device location, and AI algorithms enable the data to be processed right on the network edge, with or without an internet connection. This facilitates the processing of data within milliseconds, providing real-time feedback.
- Self-driving cars, wearable devices, security cameras, and smart home appliances are among the technologies that leverage edge AI capabilities to promptly deliver users with real-time information when it is most essential.
- Multimodal Intelligence and Agents:
- Subset of artificial intelligence that integrates information from various modalities, such as text, images, audio, and video, to build more accurate and comprehensive AI models.
- Multimodal capabilities allows to interact with users in a more natural and intuitive way. It can see, hear and speak, which means that users can provide input and receive responses in a variety of ways.
- An AI agent is a computational entity designed to act independently. It performs specific tasks autonomously by making decisions based on its environment, inputs, and a predefined goal. What separates an AI agent from an AI model is the ability to act. There are many different kinds of agents such as reactive agents and proactive agents. Agents can also act in fixed and dynamic environments. Additionally, more sophisticated applications of agents involve utilizing agents to handle data in various formats, known as multimodal agents and deploying multiple agents to tackle complex problems.
- Small Language Models (SLM) and Large Language Models (LLM):
- Small language models (SLMs) are artificial intelligence (AI) models capable of processing, understanding and generating natural language content. As their name implies, SLMs are smaller in scale and scope than large language models (LLMs).
- LLM means large language model—a type of machine learning/deep learning model that can perform a variety of natural language processing (NLP) and analysis tasks, including translating, classifying, and generating text; answering questions in a conversational manner; and identifying data patterns.
- For example, virtual assistants like Siri, Alexa, or Google Assistant use LLMs to process natural language queries and provide useful information or execute tasks such as setting reminders or controlling smart home devices.
- Vaults:
- The term “electric vaults” or “medium voltage vaults” shall be defined as any room containing electrical equipment operating above 600 volts. 1.2. Vaults shall be designed to comply with NEC 450, Part III, as a 3 hour rated structure and shall not be constructed with any flammable material.
- Switchgears:
- Broad term that describes a wide variety of switching devices that all fulfill a common need: controlling, protecting, and isolating power systems. This definition can be extended to include devices to regulate and meter a power system, circuit breakers, and similar technology.
- Switchgear contains fuses, switches, and other power conductors. However, circuit breakers are the most common component found in switchgear.
- Performs the function of controlling and metering the flow of electrical power in addiction to acting as interrupting and switching devices that protects the equipment from damage arising out of electrical fluctuations.
- There are three types of switch gears namely LV (Low voltage), MV (Medium voltage) and HV (High voltage) Switchgear.
- Circuit Breakers:
- Mechanical electrical switch designed to protect an electrical circuit from damage caused by overcurrent/overload or short circuit. Its basic function is to interrupt current flow after protective relays detect a fault.
- By definition a circuit breaker is an electrical safety device, a switch that automatically interrupts the current of an overloaded electric circuit, ground faults, or short circuits.
- Fuses:
- Single time mechanical circuit interruption in an over-current situation through fusion of a graded electrical conductor. Employed in 30KV to 100KV range.
- Electrical safety device that operates to provide overcurrent protection of an electrical circuit. Its essential component is a metal wire or strip that melts when too much current flows through it, thereby stopping or interrupting the current.
- Fuse Switch-Disconnector:
- Fuse switch disconnector combines the functions of a fuse and a switch disconnector; It provides overcurrent protection like a fuse, and it also allows for manual disconnection of the circuit for isolation purposes.
- ACB (Air Circuit Breakers):
- Uses air as insulating medium.
- Air circuit breaker is a circuit breaker for the purpose of protecting low voltage circuit, mainly for energizing and cutting off high current
- VCB (Vacuum Circuit Breakers):
- Vacuum is used as the means to protect circuit breakers.
- Circuit breaker where the arc quenching takes place in a vacuum medium. The operation of switching on and closing of current carrying contacts and interrelated arc interruption takes place in a vacuum chamber in the breaker which is called a vacuum interrupter.
- AIS (Air Insulated Switchgears):
- Air is used for insulation in a metal-clad system
- Secondary power distribution device and medium voltage switchgear that helps redistribute the power of a primary power distributor powered by a high voltage distribution transformer. AIS controls, protects and isolates electrical equipment in power transmission and distribution systems.
- GIS (Gas Insulated Switchgears):
- All working components assembled under SF6 (Sulfur Hexafluoride HV Switchgears) gas-tight casing.
- Compact metal encapsulated switchgear consisting of high-voltage components such as circuit-breakers and disconnectors, which can be safely operated in confined spaces.
- OCB (Oil Circuit Breakers):
- Vapors a portion of oil to blast a jet of oil through the arc.
- Circuit breaker which uses insulating oil as an arc quenching medium
- Hybrid Circuit Breakers:
- Combines Air-insulated and SF6 Gas-insulated technologies.
- MCB (Miniature Circuit Breakers):
- Employed in domestic households to safeguard against overload. Rated current max. 100 A.
- Electrical switch that automatically switches off the electrical circuit during an abnormal condition of the network means an overload condition as well as a faulty condition. Nowadays we use an MCB in a low-voltage electrical network instead of a fuse.
- Circuit breakers have a tripping relay mechanism, while MCB has a tripping release mechanism. Circuit breakers have a high rupturing capacity, but the MCB has a low rupturing capacity. Circuit breakers are used in High Voltage systems, while MCBs are used in Low Voltage systems.
- RCCB (Residual Current Circuit Breakers):
- To safeguard against electrical shock arising out of indirect contact and includes the detection of residual current such as earth leakage.
- Current sensing device, which can automatically measure and disconnect the circuit whenever a fault occurs in the connected circuit or the current exceeds the rated sensitivity.
- MCCB (Molded Case Circuit Breakers):
- Incorporates insulating material in the form of molded casing within circuit breaker. Rated current up to 2,500 A.
- MCCB has a higher interrupting capacity, meaning it can handle larger loads than a conventional breaker. Generally, a standard breaker is used for residential and light commercial applications, while an MCCB is suitable for industrial and heavy commercial applications.
- Disconnectors:
- Automatic switching device that offers specific isolating distance on the basis of specific requirements.
- Disconnectors (also known as Isolators) are devices which are generally operated off-load to provide isolation of main plant items for maintenance, or to isolate faulted equipment from other live equipment.
- Contactors:
- Works alike high-current switching systems but at higher voltage rates. Contactors can however not be utilized as disconnecting switches. Contactors are employed in 30KV to 100KV range.
- Special type of relay used for switching an electrical circuit on or off.
- Electrical device that is widely used for switching circuits on and off. As such, electrical contactors form a subcategory of electromagnetic switches known as relays. A relay is an electrically operated switching device that uses an electromagnetic coil to open and close a set of contacts.
- PTCB eFuse Circuit Breaker:
- Electronic micro fuse for DIN rail protecting electronically nominal currents below 1A to facilitate the clear detection of faults and supports precise fault localization and fast recovery. Response times are shorter compared to conventional fuse protection and the exact current value can be adjusted at any time
- RCD (Residual Current Devices):
- Sensitive safety device that switches off the electricity within 10 to 50 milliseconds if there is an electrical fault. An RCD is is designed to protect against the risks of electrocution and fire caused by earth faults.
- The difference between a circuit breaker and an RCD switch is the purpose of a circuit breaker is to protect the electrical systems and wiring in a home while the purpose of an RCD switch is to protect people from electrocution.
- RCBO (Residual Current Breaker with Over-Current):
- RCDs can protect against electric shocks, residual currents, and earth faults. On the other hand, RCBOs can do what RCDs can do and protect a circuit from short circuits and overload. RCBOs are essentially a combination of MCB and RCCB.
- An RCBO protects electrical equipment from two types of faults; residual current and over current. Residual current, or Earth leakage as it can sometimes be referred to, is when there is a break in the circuit that could be caused by faulty electrical wiring or if the wire is accidentally cut.
- Ring Main Unit (RMU):
- Medium voltage, gas-insulated, fully sealed cabinet used to measure, connect, and integrate transformer protection functions with a fixed type breaker. Ring Main Units are safe, reliable, low-maintenance, and easy to replace switchgear.
- A ring main unit (RMU) is a factory assembled, metal enclosed set of switchgear used at the load connection points of a ring-type distribution network.
- Enclosure – Load Center – Panel Board – Switch Board – Distribution Cabinet – Distribution Box:
- Enclosure is the general term referring to any protective housing for electrical or electronic equipment.
- A load center is used in residential and light commercial applications to distribute electricity supplied by the utility company throughout the home or building to feed all the branch circuits. Each branch circuit is protected by the circuit breaker housed in the load center. In the event of a short circuit or an overload on a branch circuit, the circuit breaker will cut the power before any potential property damage or personal injury can occur.
- A load center provides similar functionality in a power distribution system as a switchboard and a panelboard. As far as UL and the NEC standards are concerned, there is no difference between a panelboard and a load center.
- However, Panelboards are typically deeper than load centers and can accommodate both bolt-on circuit breakers as well as plug-in breakers, whereas a load center is limited to plug-in breakers.
- Switchboards are often the typical choice for industrial establishments. These panelboards generally house circuit breakers that can manage and supply electricity for machines with high-voltage demands.
- Panelboards are only accessible from the front (as mentioned above), but switchboards allow rear access as well.
- In terms of use, distribution boxes are generally used for households, and distribution cabinets are mostly used for centralized power supply. Distribution boxes and cabinets are complete sets of equipment. Distribution boxes are low-voltage complete sets of equipment. Cabinets have both high and low voltages.

- Solid-State Circuit Breakers:
- Solid-state device, electronic device in which electricity flows through solid semiconductor crystals (silicon, gallium arsenide, germanium) rather than through vacuum tubes.
- The solid-state breaker concept replaces the traditional moving parts of an electromechanical circuit breaker with semiconductors and advanced software algorithms that control the power and can interrupt extreme currents faster than ever before.
- Pad-mount Switchgear:
- The pad-mount switchgear is made from the same modular switch and interrupter components as the vault switchgear. This means all components are sealed, submersible and protected, so you don’t have to worry about tracking, animal infestation, corrosion or the effects of condensation inside the enclosure.


