Siemens – Siemens and Microsoft partner to drive cross-industry AI adoption
- Companies introduce Siemens Industrial Copilot, a generative AI-powered assistant, designed to enhance human-machine collaboration and boost productivity.
- Companies will work together to build additional copilots for manufacturing, infrastructure, transportation, and healthcare industries.
- Leading automotive supplier, Schaeffler AG, is an early adopter of Siemens Industrial Copilot.
- In addition, the Siemens Teamcenter app for Microsoft Teams will be generally available in December 2023 and accelerate innovation across the product lifecycle.
Microsoft and Siemens are deepening their partnership by bringing the benefits of generative AI to industries worldwide. As a first step, the companies are introducing Siemens Industrial Copilot, an AI-powered jointly developed assistant aimed at improving human-machine collaboration in manufacturing. In addition, the launch of the integration between Siemens Teamcenter software for product lifecycle management and Microsoft Teams will further pave the way to enabling the industrial metaverse. It will simplify virtual collaboration of design engineers, frontline workers, and other teams across business functions.

Siemens and Microsoft partner to drive cross-industry AI adoption. Picture: Microsoft
“With this next generation of AI, we have a unique opportunity to accelerate innovation across the entire industrial sector,” said Satya Nadella, Chairman and CEO, Microsoft. “We’re building on our longstanding collaboration with Siemens and bringing together AI advances across the Microsoft Cloud with Siemens’ industrial domain expertise to empower both frontline and knowledge workers with new, AI-powered tools, starting with Siemens Industrial Copilot.”
“Together with Microsoft, our shared vision is to empower customers with the adoption of generative AI,” says Roland Busch, CEO of Siemens AG. “This has the potential to revolutionize the way companies design, develop, manufacture, and operate. Making human-machine collaboration more widely available allows engineers to accelerate code development, increase innovation and tackle skilled labor shortages.”
A new era of human-machine collaboration
Siemens Industrial Copilot will allow users to rapidly generate, optimize and debug complex automation code, and significantly shorten simulation times. This will reduce a task that previously took weeks to minutes. The copilot ingests automation and process simulation information from Siemens’ open digital business platform, Siemens Xcelerator, and enhances it with Microsoft’s Azure OpenAI Service. Customers maintain full control over their data, and it is not used to train underlying AI models.
Siemens Industrial Copilot promises to boost productivity and efficiency across the industrial lifecycle. Using natural language, maintenance staff can be assisted with detailed repair instructions and engineers with quick access to simulation tools.
The vision: Copilots for all industries
The companies envision AI copilots assisting professionals in various industries, including manufacturing, infrastructure, transportation, and healthcare. Numerous copilots are already planned in the manufacturing sectors, such as automotive, consumer package goods and machine building.
Schaeffler AG, a leading automotive supplier, is among the first in the automotive industry to embrace generative AI in the engineering phase. This helps its engineers to generate reliable code for programming industrial automation systems such as robots. In addition, the company intends to incorporate the Siemens Industrial Copilot during their own operations, aiming to significantly reduce downtimes, and also for their clients at a later stage.
”With this joint pilot, we’re stepping into a new age of productivity and innovation. This Siemens Industrial Copilot will help our team work more efficiently, reduce repetitive tasks, and unleash creativity. We’re excited to partner with Siemens and Microsoft on this project”. Klaus Rosenfeld, CEO of Schaeffler Group.
Siemens Industrial Copilot Coding
Generative AI facilitates virtual collaboration
To bring virtual collaboration across teams to the next level, Teamcenter for Microsoft Teams will be generally available beginning December 2023. This new app uses the latest advances in generative AI to connect functions across the product design and manufacturing lifecycle such as frontline workers to engineering teams. It connects Siemens’ Teamcenter software for product lifecycle management (PLM) with Microsoft’s collaboration platform Teams to make data more accessible for factory and field service workers. This will enable millions of workers who do not have access to PLM tools today to contribute to the design and manufacturing process more easily as part of their daily work.
Siemens will share more details on Siemens Industrial Copilot at the SPS expo in Nuremberg, Germany, in November 2023.

Siemens and Microsoft partner to drive cross-industry AI adoption. Picture: Microsoft
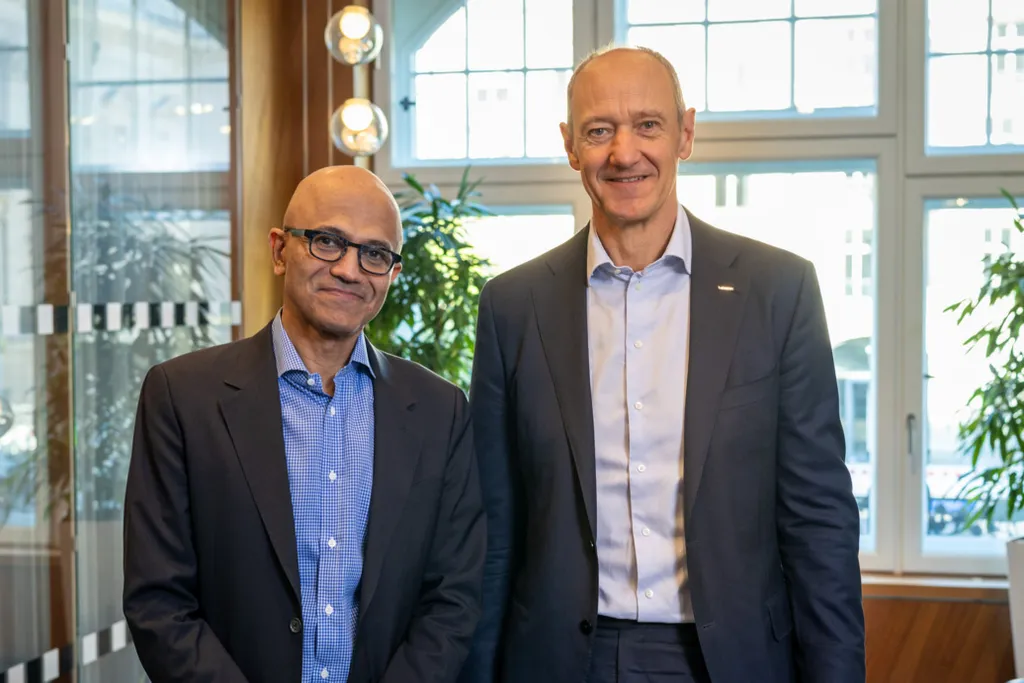

Satya Nadella, Chairman and CEO, Microsoft and Roland Busch, CEO of Siemens AG. Picture: Microsoft

Manufacturing in the automotive industry. Picture: Siemens AG

Manufacturing in the chemical industry. Picture: Siemens AG

Siemens and Microsoft partner to drive cross-industry AI adoption. Picture: Microsoft

Satya Nadella, Chairman and CEO, Microsoft and Roland Busch, CEO of Siemens AG. Picture: Microsoft

Manufacturing in the automotive industry. Picture: Siemens AG

Manufacturing in the chemical industry. Picture: Siemens AG

Siemens and Microsoft partner to drive cross-industry AI adoption. Picture: Microsoft
SourceSIEMENS
EMR Analysis
More information on Siemens: See the full profile on EMR Executive Services
More information on Dr. Roland Busch (President and Chief Executive Officer, Siemens AG): See the full profile on EMR Executive Services
More information on Siemens Industrial Copilot: https://www.siemens.com/global/en/company/stories/digital-transformation/industrial-copilot.html + Chatbots with brains packed with artificial intelligence (AI) can revolutionize the jobs of programming and automation component diagnosis. The revolution is being started by the Industrial Copilot that Siemens has developed with the help of Microsoft: The copilot writes the programming code for machinery in factories and helps track down software bugs. This application will soon go on sale around the world – at such places as Siemens Xcelerator.

At the moment, Siemens is developing and testing its Industrial Copilot, a technology that helps automation engineers do their jobs and will be offered to users on Siemens Xcelerator. The open platform assists industrial customers with their digital transformation – offering a selected portfolio of networked hardware and software, a high-performance ecosystem of partners and a comprehensive marketplace of applications.
More information on Siemens Teamcenter: https://blogs.sw.siemens.com/teamcenter/ + Teamcenter® software is a modern, adaptable product lifecycle management (PLM) system that connects people and processes, across functional silos, with a digital thread for innovation.
More information on Xcelerator by Siemens: https://www.sw.siemens.com/en-US/digital-transformation/ + Xcelerator provides the engineering and manufacturing software, services and application development platform to blur the boundaries between industry domains. Companies can use this technology today to build the products of tomorrow. Turn complexity into your competitive advantage with Xcelerator.
Siemens Xcelerator consists of three pillars:
- Portfolio: A curated, modular portfolio of IOT-enabled hardware and software based on standard application programming interfaces, facilitating the integration of information technology (IT) and operational technology (OT).
- Ecosystem: A growing ecosystem of partners.
- Marketplace: Interactions and transactions among customers, partners and developers.
More information on Microsoft: https://www.microsoft.com + Microsoft (Nasdaq “MSFT” @microsoft) enables digital transformation for the era of an intelligent cloud and an intelligent edge. Its mission is to empower every person and every organization on the planet to achieve more. Microsoft refers to Microsoft Corp. and its affiliates, including Microsoft Mobile Oy, a subsidiary of Microsoft. Microsoft Mobile Oy develops, manufactures and distributes Nokia X mobile phones and other devices.
More information on Satya Nadella (Chairman & Chief Executive Officer, Microsoft): https://news.microsoft.com/exec/satya-nadella/ + https://www.linkedin.com/in/satyanadella/
More information on Microsoft Azure: https://azure.microsoft.com/https://azure.microsoft.com/ + The Azure cloud platform is more than 200 products and cloud services designed to help you bring new solutions to life—to solve today’s challenges and create the future. Build, run, and manage applications across multiple clouds, on-premises, and at the edge, with the tools and frameworks of your choice.
More information on Microsoft Azure OpenAI Service: https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/products/cognitive-services/openai-service + Apply large language models and generative AI to a variety of use cases..
Take advantage of large-scale, generative AI models with deep understandings of language and code to enable new reasoning and comprehension capabilities for building cutting-edge applications. Apply these coding and language models to a variety of use cases, such as writing assistance, code generation, and reasoning over data. Detect and mitigate harmful use with built-in responsible AI and access enterprise-grade Azure security.
More information on Schaeffler AG: https://www.schaeffler.com/en/ + The Schaeffler Group has been driving forward groundbreaking inventions and developments in the field of motion technology for over 75 years. With innovative technologies, products, and services for electric mobility, CO₂-efficient drives, chassis solutions, Industry 4.0, digitalization, and renewable energies, the company is a reliable partner for making motion more efficient, intelligent, and sustainable – over the entire life cycle. The motion technology company manufactures high-precision components and systems for drive train and chassis applications as well as rolling and plain bearing solutions for a large number of industrial applications.
The Schaeffler Group generated sales of EUR 15.8 billion in 2022. With around 84,000 employees, the Schaeffler Group is one of the world’s largest family-owned companies. With more than 1,250 patent applications in 2022, Schaeffler is Germany’s fourth most innovative company according to the DPMA (German Patent and Trademark Office).
More information on Klaus Rosenfeld (Chief Executive Officer, Schaeffler AG): https://www.schaeffler.com/en/group/executive-board/
More information on SPS 2023 (Smart Production Solutions) Germany (14-16 November 2023, Nüremberg, Germany): https://sps.mesago.com/nuernberg/en.html + Bringing Automation to Life.
The SPS is the industry highlight of the automation sector and, with its unique concept, represents the complete spectrum of smart and digital automation – from simple sensors to intelligent solutions, from what is feasible today to the vision of a comprehensively digitized industrial world.
EMR Additional Notes:
- AI – Artificial Intelligence:
- https://searchenterpriseai.techtarget.com/definition/AI-Artificial-Intelligence +
- Artificial intelligence is the simulation of human intelligence processes by machines, especially computer systems. Specific applications of AI include expert systems, natural language processing, speech recognition and machine vision.
- As the hype around AI has accelerated, vendors have been scrambling to promote how their products and services use AI. Often what they refer to as AI is simply one component of AI, such as machine learning. AI requires a foundation of specialized hardware and software for writing and training machine learning algorithms. No one programming language is synonymous with AI, but a few, including Python, R and Java, are popular.
- In general, AI systems work by ingesting large amounts of labeled training data, analyzing the data for correlations and patterns, and using these patterns to make predictions about future states. In this way, a chatbot that is fed examples of text chats can learn to produce lifelike exchanges with people, or an image recognition tool can learn to identify and describe objects in images by reviewing millions of examples.
- AI programming focuses on three cognitive skills: learning, reasoning and self-correction.
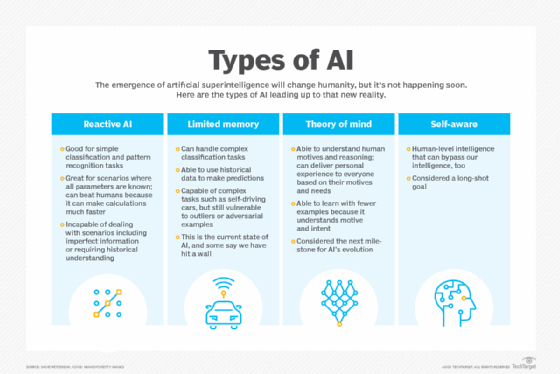
- What are the 4 types of artificial intelligence?
- Type 1: Reactive machines. These AI systems have no memory and are task specific. An example is Deep Blue, the IBM chess program that beat Garry Kasparov in the 1990s. Deep Blue can identify pieces on the chessboard and make predictions, but because it has no memory, it cannot use past experiences to inform future ones.
- Type 2: Limited memory. These AI systems have memory, so they can use past experiences to inform future decisions. Some of the decision-making functions in self-driving cars are designed this way.
- Type 3: Theory of mind. Theory of mind is a psychology term. When applied to AI, it means that the system would have the social intelligence to understand emotions. This type of AI will be able to infer human intentions and predict behavior, a necessary skill for AI systems to become integral members of human teams.
- Type 4: Self-awareness. In this category, AI systems have a sense of self, which gives them consciousness. Machines with self-awareness understand their own current state. This type of AI does not yet exist.
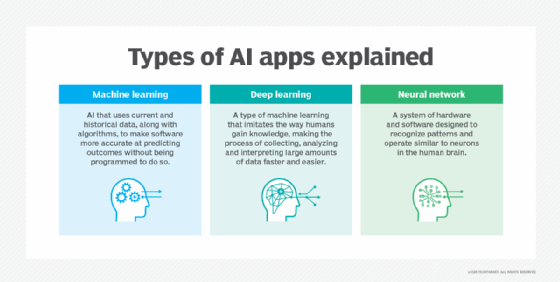
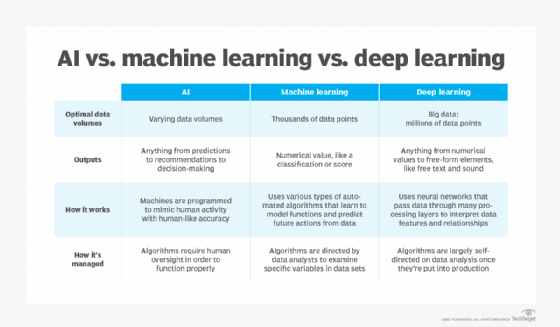
- Machine Learning:
- Developed to mimic human intelligence. It lets the machines learn independently by ingesting vast amounts of data and detecting patterns. Many ML algorithms use statistics formulas and big data to function.
- Type of artificial intelligence (AI) that allows software applications to become more accurate at predicting outcomes without being explicitly programmed to do so. Machine learning algorithms use historical data as input to predict new output values.
- Recommendation engines are a common use case for machine learning. Other popular uses include fraud detection, spam filtering, malware threat detection, business process automation (BPA) and Predictive maintenance.
- Classical machine learning is often categorized by how an algorithm learns to become more accurate in its predictions. There are four basic approaches: supervised learning, unsupervised learning, semi-supervised learning and reinforcement learning. The type of algorithm data scientists choose to use depends on what type of data they want to predict.
- Deep Learning:
- Subset of machine learning. Deep learning enabled much smarter results than were originally possible with machine learning. Consider the face recognition example.
- Deep learning makes use of layers of information processing, each gradually learning more and more complex representations of data. The early layers may learn about colors, the next ones learn about shapes, the following about combinations of those shapes, and finally actual objects. Deep learning demonstrated a breakthrough in object recognition.
- Deep learning is currently the most sophisticated AI architecture we have developed.
- Computer Vision:
- Computer vision is a field of artificial intelligence (AI) that enables computers and systems to derive meaningful information from digital images, videos and other visual inputs — and take actions or make recommendations based on that information.
- The most well-known case of this today is Google’s Translate, which can take an image of anything — from menus to signboards — and convert it into text that the program then translates into the user’s native language.
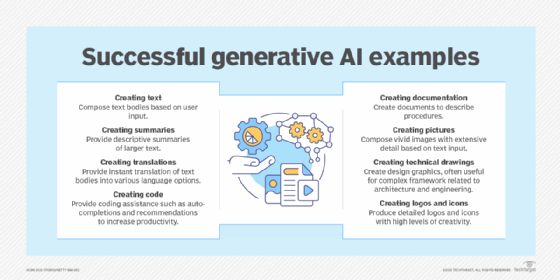
- Generative AI:
- Generative AI technology generates outputs based on some kind of input – often a prompt supplied by a person. Some GenAI tools work in one medium, such as turning text inputs into text outputs, for example. With the public release of ChatGPT in late November 2022, the world at large was introduced to an AI app capable of creating text that sounded more authentic and less artificial than any previous generation of computer-crafted text.
- https://searchenterpriseai.techtarget.com/definition/AI-Artificial-Intelligence +
- Metaverse:
- The first use of the term ‘metaverse’ was in the 1992 science fiction novel “Snow Crash”, by Neal Stephenson, which described a single virtual world separate from the physical world.
- In the broadest terms, the metaverse is understood as a graphically rich virtual space, with some degree of verisimilitude, where people can work, play, shop, socialize — in short, do the things humans like to do together in real life (or, perhaps more to the point, on the internet).
- The technologies companies refer to when they talk about “the metaverse” can include virtual reality—characterized by persistent virtual worlds that continue to exist even when you’re not playing—as well as augmented reality that combines aspects of the digital and physical worlds.
- Basically, a place parallel to the physical world, where you spend your digital life. A place where you and other people have an avatar, and you interact with them through their avatars.
- The Metaverse represents a highly interactive three-dimensional virtual world. Like the real world, users can trade land, buildings, and other digital assets in the Metaverse and explore the space using their personalized avatars.
- Examples: Hyundai Motor Company debuted Hyundai Mobility Adventure, a metaverse experience on gaming platform Roblox. Gamers’ avatars can experience Hyundai future mobility projects and current products. And last year, Warner Bros. Pictures hosted a virtual party on Roblox to market its movie In the Heights.
- Bloomberg Intelligence tells us that the value of the metaverse is expected to reach $800 billion by the middle 2020s with that figure climbing to $2.5 trillion by 2030.
- Following Meta, the metaverse is the next evolution in social connection and the successor to the mobile Internet.
- Industrial Metaverse:
- The industrial metaverse is a network of digital twins that links physical assets and the digital world. It enables manufacturers to connect their digital twins with their customers and suppliers so they can work together and get insights based on real time data.
- On one side, we have Industry 4.0 (Industrial IoT or IIoT) which has been gathering data from equipment and environments for many years. This data is increasingly stored in the cloud and accessed through an off-the-shelf IoT provider, such as Amazon’s AWS or Microsoft’s Azure. On the other side, we have the 3D world of gaming technology, augmented/virtual/mixed realities, and CAD. Combining the two leads to an immersive environment where IoT data can be accessed in new and innovative ways.
- Digital worlds based on real-time data will allow corporations to have multiple iterations and simulations of themselves. Lessons learned and breakthroughs discovered in the Industrial Metaverse will provide feedback into reality, enabling companies to change real-world parameters to optimise everything!
- The Industrial Metaverse is “basically” a Digital Twin
- Simulations in a metaverse environment could allow manufacturers to test thousands of potential scenarios for their ecosystems to explore different strategies.
- Product Lifecycle Management (PLM):
- At the most fundamental level, product lifecycle management (PLM) is the strategic process of managing the complete journey of a product from initial ideation, development, service, and disposal. Put another way, PLM means managing everything involved with a product from cradle to grave.


