Southwire – Southwire Company Announces Investment in HData
In support of Southwire’s strategic investment initiative, the company is pleased to announce an investment in HData, a software company that automates regulatory data analysis.
HData, based in Birmingham, Ala., digitizes regulated energy industry data by automating access to critical analytics for electric, oil and gas companies and their regulators.
“Our investment in HData gives us a valuable partnership in the rapidly developing world of AI for business intelligence,” said Charles Hume, managing director of Southwire Technology Ventures. “As a leading supplier to the utility industry, we are excited about the insights that our partnership with HData will provide into the industry.”
As a part of this investment, Southwire will join HData’s Advisory Board, represented by Donna Ward, gaining further insights into the utility industry.
“I am excited to be part of Southwire’s engagement with HData,” said Donna Ward, Southwire’s vice president of utility sales and commercial marketing. “HData’s technology will fundamentally improve regulatory tasks and will be an asset to the Energy industry.”
HData’s proprietary software can scan and extract insights from Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) reports, turning mutli-thousand-page PDFs into actionable charts, comparisons and insights.
“We couldn’t be prouder to welcome Southwire to HData as both a customer and a Series A investor,” said Hudson Hollister, founder and CEO of HData. “This new partnership underscores the value of our regulatory data platform to supply crucial intelligence for a fast-transitioning energy industry, including leading suppliers shaping the future of power delivery like Southwire.”
HData joins a portfolio of investments managed by the Southwire Technology Ventures team. This team collaborates with pioneering startups to build the future of smart power within the realms of smart buildings, electric mobility and the grid of the future. To learn more, visit the Southwire Technology Ventures team webpage.
SourceSouthwire
EMR Analysis
More information on Southwire: See the full profile on EMR Executive Services
More information on Rich Stinson (President and Chief Executive Officer, Southwire): See the full profile on EMR Executive Services
More information on Donna Ward (Vice President, Utility Sales and Commercial Marketing, Southwire): See the full profile on EMR Executive Services
More information on Southwire Technology Ventures: https://www.southwire.com/technology-ventures + SWTV collaborates with pioneering startups to build the future of smart power. We invest in and partner with early-stage ventures exploring digital power, smart buildings, electric mobility and the grid of the future.
More information on Charles Hume (Managing Director, Southwire Technology Ventures, Southwire): See the full profile on EMR Executive Services
More information on HData by Southwire: https://www.hdata.us/ + HData helps you access and analyze energy regulatory information instantly. Reduce the burden of regulatory work while enhancing the business value of energy data analysis.
HData is the only RegTech company delivering streamlined compliance and business intelligence to the U.S. energy industry. Our mission is to digitize the interface between the public and private sectors. We automate manual processes for people who comply with regulations, enforce regulations, and use regulatory data.
More information on Hudson Hollister (Founder and Chief Executive Officer, HData, Southwire): See the full profile on EMR Executive Services
More information on Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC): https://www.ferc.gov/ + The Federal Energy Regulatory Commission, or FERC, is an independent agency that regulates the interstate transmission of natural gas, oil, and electricity. FERC also regulates natural gas and hydropower projects. .
FERC’s Mission: Assist consumers in obtaining reliable, safe, secure, and economically efficient energy services at a reasonable cost through appropriate regulatory and market means, and collaborative efforts.
More information on Willie L. Phillips (Chairman, Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC)): https://www.ferc.gov/about/commission-members + https://www.linkedin.com/in/willie-phillips-36b0307/
EMR Additional Notes:
- AI – Artificial Intelligence:
- https://searchenterpriseai.techtarget.com/definition/AI-Artificial-Intelligence +
- Artificial intelligence is the simulation of human intelligence processes by machines, especially computer systems.
- As the hype around AI has accelerated, vendors have been scrambling to promote how their products and services use AI. Often what they refer to as AI is simply one component of AI, such as machine learning. AI requires a foundation of specialized hardware and software for writing and training machine learning algorithms. No one programming language is synonymous with AI, but well a few, including Python, R and Java, are popular.
- In general, AI systems work by ingesting large amounts of labeled training data, analyzing the data for correlations and patterns, and using these patterns to make predictions about future states. In this way, a chatbot that is fed examples of text chats can learn to produce lifelike exchanges with people, or an image recognition tool can learn to identify and describe objects in images by reviewing millions of examples.
- AI programming focuses on three cognitive skills: learning, reasoning and self-correction.
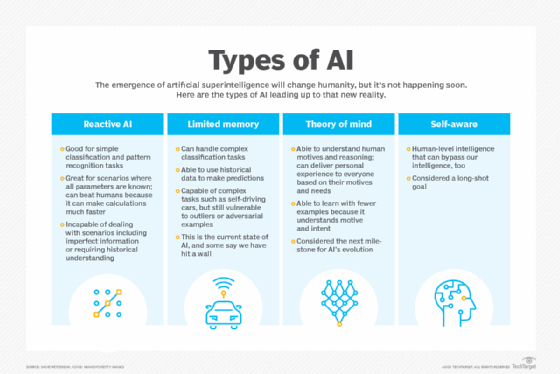
- What are the 4 types of artificial intelligence?
- Type 1: Reactive machines. These AI systems have no memory and are task specific. An example is Deep Blue, the IBM chess program that beat Garry Kasparov in the 1990s. Deep Blue can identify pieces on the chessboard and make predictions, but because it has no memory, it cannot use past experiences to inform future ones.
- Type 2: Limited memory. These AI systems have memory, so they can use past experiences to inform future decisions. Some of the decision-making functions in self-driving cars are designed this way.
- Type 3: Theory of mind. Theory of mind is a psychology term. When applied to AI, it means that the system would have the social intelligence to understand emotions. This type of AI will be able to infer human intentions and predict behavior, a necessary skill for AI systems to become integral members of human teams.
- Type 4: Self-awareness. In this category, AI systems have a sense of self, which gives them consciousness. Machines with self-awareness understand their own current state. This type of AI does not yet exist.
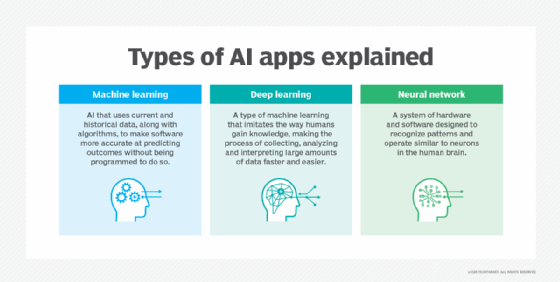
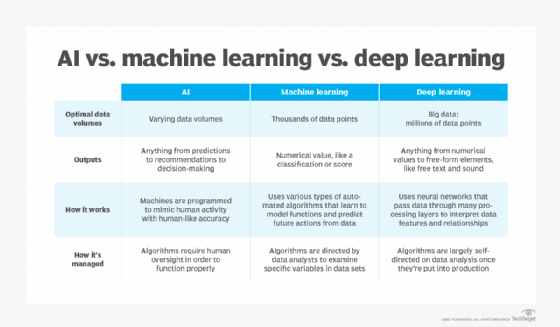
- Machine Learning (ML):
- Developed to mimic human intelligence, it lets the machines learn independently by ingesting vast amounts of data, statistics formulas and detecting patterns.
- ML allows software applications to become more accurate at predicting outcomes without being explicitly programmed to do so.
- ML algorithms use historical data as input to predict new output values.
- Recommendation engines are a common use case for ML. Other uses include fraud detection, spam filtering, business process automation (BPA) and predictive maintenance.
- Classical ML is often categorized by how an algorithm learns to become more accurate in its predictions. There are four basic approaches: supervised learning, unsupervised learning, semi-supervised learning and reinforcement learning.
- Deep Learning (DL):
- Subset of machine learning, Deep Learning enabled much smarter results than were originally possible with ML. Face recognition is a good example.
- DL makes use of layers of information processing, each gradually learning more and more complex representations of data. The early layers may learn about colors, the next ones about shapes, the following about combinations of those shapes, and finally actual objects. DL demonstrated a breakthrough in object recognition.
- DL is currently the most sophisticated AI architecture we have developed.
- Computer Vision (CV):
- Computer vision is a field of artificial intelligence that enables computers and systems to derive meaningful information from digital images, videos and other visual inputs — and take actions or make recommendations based on that information.
- The most well-known case of this today is Google’s Translate, which can take an image of anything — from menus to signboards — and convert it into text that the program then translates into the user’s native language.
- Machine Vision (MV):
- Machine Vision is the ability of a computer to see; it employs one or more video cameras, analog-to-digital conversion and digital signal processing. The resulting data goes to a computer or robot controller. Machine Vision is similar in complexity to Voice Recognition.
- MV uses the latest AI technologies to give industrial equipment the ability to see and analyze tasks in smart manufacturing, quality control, and worker safety.
- Computer Vision systems can gain valuable information from images, videos, and other visuals, whereas Machine Vision systems rely on the image captured by the system’s camera. Another difference is that Computer Vision systems are commonly used to extract and use as much data as possible about an object.
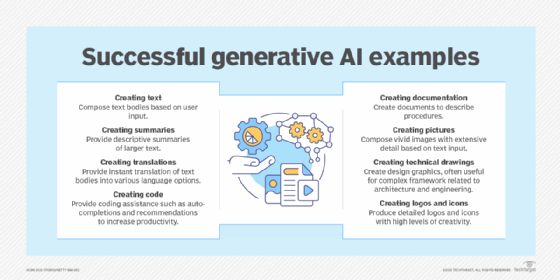
- Generative AI (GenAI):
- Generative AI technology generates outputs based on some kind of input – often a prompt supplied by a person. Some GenAI tools work in one medium, such as turning text inputs into text outputs, for example. With the public release of ChatGPT in late November 2022, the world at large was introduced to an AI app capable of creating text that sounded more authentic and less artificial than any previous generation of computer-crafted text.
- https://searchenterpriseai.techtarget.com/definition/AI-Artificial-Intelligence +
- Edge AI Technology:
- Edge artificial intelligence refers to the deployment of AI algorithms and AI models directly on local edge devices such as sensors or Internet of Things (IoT) devices, which enables real-time data processing and analysis without constant reliance on cloud infrastructure.
- Simply stated, edge AI, or “AI on the edge“, refers to the combination of edge computing and artificial intelligence to execute machine learning tasks directly on interconnected edge devices. Edge computing allows for data to be stored close to the device location, and AI algorithms enable the data to be processed right on the network edge, with or without an internet connection. This facilitates the processing of data within milliseconds, providing real-time feedback.
- Self-driving cars, wearable devices, security cameras, and smart home appliances are among the technologies that leverage edge AI capabilities to promptly deliver users with real-time information when it is most essential.
- Grid, Microgrids and DERs:
- The power grid is a network for delivering electricity to consumers. The power grid includes generator stations, transmission lines and towers, and individual consumer distribution lines.
- The grid constantly balances the supply and demand for the energy that powers everything from industry to household appliances.
- Electric grids perform three major functions: power generation, transmission, and distribution.
- A microgrid is a small-scale power grid that can operate independently or collaboratively with other small power grids. The practice of using microgrids is known as distributed, dispersed, decentralized, district or embedded energy production.
- Smart Grid is any electrical grid + IT at all levels . Micro Grid is a group of interconnected loads and DERs (Distributed energy resources) within a clearly defined electrical and geographical boundaries witch acts as a single controllable entity with respect to the main grid.
- Distributed energy resources (DERs) are small-scale electricity supply (typically in the range of 3 kW to 50 MW) or demand resources that are interconnected to the electric grid. They are power generation resources and are usually located close to load centers, and can be used individually or in aggregate to provide value to the grid.
- Common examples of DERs include rooftop solar PV units, natural gas turbines, microturbines, wind turbines, biomass generators, fuel cells, tri-generation units, battery storage, electric vehicles (EV) and EV chargers, and demand response applications.
- Distributed energy resources management systems (DERMS) are platforms which helps mostly distribution system operators (DSO) manage their grids that are mainly based on distributed energy resources (DER).
- DERMS are used by utilities and other energy companies to aggregate a large energy load for participation in the demand response market. DERMS can be defined in many ways, depending on the use case and underlying energy asset.


